Seawater corrosion presents significant challenges to industrial equipment operating in marine environments. The combination of salt, moisture, and oxygen accelerates the corrosion process, leading to premature wear and failure of components. For industries reliant on rotating machinery, such as marine, offshore energy, and chemical processing sectors, this issue is particularly critical. Equipment exposed to seawater, including pumps, valves, and rotary joints, faces constant degradation, which can result in downtime, costly repairs, and compromised safety. In these conditions, the need for durable, corrosion-resistant components is paramount. Rotary joints, which play a crucial role in transferring fluids between stationary and rotating parts, are especially vulnerable to the harsh effects of saltwater. Without proper protection, the corrosive environment can cause these components to fail, impacting the efficiency and longevity of the equipment.
Why Seawater-Resistant Rotary Joints Matter
Corrosion Risks in Marine Environments
Marine environments are inherently corrosive due to the presence of saltwater, which accelerates the degradation of materials. Saltwater’s combination of chloride ions, oxygen, and moisture creates a highly aggressive environment that can lead to various forms of corrosion in industrial equipment. For components like rotary joints, which are used to transfer fluids between stationary and rotating parts, this environment can be particularly harsh. Common corrosion phenomena in marine environments include pitting corrosion, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking, all of which can compromise the integrity and performance of machinery.
Pitting Corrosion: This occurs when localized areas on the surface of a material begin to corrode more rapidly than surrounding areas, forming small pits or cavities. Pitting is particularly damaging because it is difficult to detect until significant material loss has occurred. In rotary joints, this can lead to leakages or failures in sealing surfaces, compromising their function.
Crevice Corrosion: Crevices between two materials or surfaces, such as gaskets or seals, can trap saltwater and moisture. The stagnant environment within these crevices creates a differential electrochemical reaction, leading to accelerated corrosion. In rotary joints, crevice corrosion often forms around the seals and connections, undermining their durability.
Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC): This form of corrosion occurs when tensile stress interacts with a corrosive environment, leading to the development of cracks. In marine environments, materials under constant stress, such as those in rotating machinery, are vulnerable to SCC, which can result in catastrophic failure if not mitigated.
Without adequate protection, these forms of corrosion can lead to the early degradation of rotary joints, causing leakage, component failure, and operational downtime. These risks are especially prevalent in subsea operations, where the equipment is exposed to saltwater pressures and conditions for prolonged periods.
Case Study: Failures in Subsea Operations Without Proper Protection
A notable example of the critical importance of corrosion-resistant rotary joints is seen in subsea operations, where failure to use appropriately protected components has led to operational breakdowns. The Macartney Model 173, a well-known rotary joint used in marine and subsea applications, has faced significant challenges in environments where corrosion protection was inadequate. These joints are tasked with transferring fluids under high pressure and in direct contact with seawater. However, when they were not designed or maintained with proper corrosion-resistant materials, issues like leakage, premature wear, and ultimately, system failures occurred.
In one such case, a subsea oil rig experienced significant operational delays when several rotary joints failed due to saltwater-induced corrosion. The failure of these components led to hydraulic fluid leakage, which in turn, affected the rig’s cooling system, resulting in overheating of critical machinery. The cost of repairs, system downtime, and the loss of production was substantial. This case highlights the critical role that corrosion-resistant rotary joints play in ensuring the smooth and safe operation of subsea systems. Without these specialized components, industries that operate in saltwater environments risk significant operational disruptions and safety hazards.
Performance Demands
To operate efficiently and safely in marine environments, seawater-resistant rotary joints must meet specific performance requirements. These demands are a result of the extreme conditions in which these components must function.
High-Pressure Resistance: Seawater-resistant rotary joints are often subjected to high-pressure environments, particularly in offshore and subsea applications. The joints must be able to withstand the pressures associated with deep-sea operations or high-flow systems. The materials used in these joints, such as corrosion-resistant alloys and high-strength polymers, must be capable of maintaining their structural integrity under constant pressure. The ability to resist deformation, leakage, and failure under high pressure is critical to the safety and longevity of offshore platforms, subsea pipelines, and other marine systems. Any failure in this context can result in catastrophic consequences, including oil spills or system shutdowns.
Compatibility with Seawater, Oils, and Hydraulic Fluids: Seawater-resistant rotary joints must also exhibit excellent compatibility with a wide range of fluids they encounter, including seawater, oils, and hydraulic fluids. These fluids can be chemically aggressive, and their interaction with metals or seals can lead to degradation over time. A high-quality rotary joint will be designed to resist corrosion not just from seawater, but also from the oils and hydraulic fluids commonly used in these environments. The seals, bearings, and other components must be resistant to chemical attack, erosion, and wear, while still allowing for smooth fluid transfer without leakage or loss of pressure.
The materials used in these joints must be able to resist oxidation and pitting caused by seawater, while also handling the varying chemical compositions of hydraulic and lubricating fluids. Seals and gaskets must be made from elastomers or composites that are resistant to swelling, cracking, or hardening when exposed to these fluids. In the case of offshore drilling or subsea mining operations, these rotary joints must remain operational in the face of constant exposure to harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures.
In marine and subsea environments, seawater-resistant rotary joints are essential to maintaining the integrity, safety, and efficiency of industrial systems. These components must be designed to withstand the corrosive effects of saltwater, the pressure of deep-sea operations, and the diverse range of fluids encountered in such environments. Without these specialized rotary joints, industries operating in marine settings face the risk of significant equipment failures, costly downtime, and safety hazards. By using advanced materials and corrosion-resistant coatings, these rotary joints can provide long-term performance and reliability, ensuring that critical systems continue to function smoothly in even the most challenging environments.

Key Features of Seawater-Resistant Rotary Joints
Seawater-resistant rotary joints are designed to provide durability and reliable performance in challenging marine environments. These rotary joints are equipped with key features that enhance their ability to withstand the corrosive effects of saltwater, high-pressure conditions, and the demands of fluid and data transfer. The following are some of the crucial features that contribute to the superior performance of seawater-resistant rotary joints.
Material Selection
The materials used in the construction of seawater-resistant rotary joints are critical to their ability to resist corrosion and function effectively in marine environments.
Stainless Steel (316 Grade): One of the most commonly used materials in seawater-resistant rotary joints is 316-grade stainless steel. Known for its superior resistance to chloride-induced corrosion, this material is highly effective in resisting the harsh effects of saltwater exposure. It provides excellent protection against pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking. This makes it an ideal choice for rotary joints used in marine environments, subsea applications, and other offshore operations. The DSTI GPS and Macartney models both utilize 316-grade stainless steel for their robust, corrosion-resistant properties. This material ensures that the rotary joints can withstand the aggressive nature of seawater and operate efficiently over extended periods.
Aluminum Alloys: For applications that require lightweight materials, aluminum alloys offer an attractive alternative. While aluminum alloys may not provide the same level of chloride resistance as stainless steel, they still offer good corrosion resistance and are much lighter, making them ideal for industries such as aerospace and robotics. In specific configurations, DSTI incorporates aluminum alloys in their rotary joints, where the weight-to-strength ratio is a significant design consideration. These joints are perfect for systems where weight savings are crucial, such as in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or robotic arms operating in coastal environments.
Grand Slip Rings’ Offerings: Grand provides high-performance rotary joints and military slip rings using corrosion-resistant materials, ensuring that these components can perform effectively in demanding environments. By incorporating high-grade materials that resist corrosion, Grand ensures that their rotary joints and slip rings maintain integrity even when exposed to saltwater, oils, and other corrosive fluids. This makes them ideal for use in military applications, where reliability is paramount.
Advanced Sealing Technology
The sealing technology in seawater-resistant rotary joints plays a crucial role in preventing fluid leakage, ensuring long-term performance, and minimizing maintenance needs.
Leak-Proof Designs: Many modern rotary joints, feature advanced leak-proof designs that prevent fluid escape. These systems are engineered to operate under high-pressure conditions, where seals are under constant stress. The leak-proof design ensures that even under extreme conditions, fluids are securely contained, preventing contamination, system failures, and costly maintenance. This feature is especially important in marine environments, where leaks could have significant environmental and operational impacts.
Replaceable Seals for Extended Lifespan: Another important feature is the use of replaceable seals. Seals in rotary joints are often the first components to wear out due to the constant motion, pressure, and exposure to fluids. However, with replaceable seals, systems can be maintained and restored to full functionality without replacing the entire rotary joint. This extends the lifespan of the equipment and reduces long-term costs. For example, Grand’s Waterproof Slip Rings offer replaceable seals that ensure continuous performance even in the harshest environments, providing additional value and longevity to the rotary joint.
Multi-Channel Configurations
Seawater-resistant rotary joints are increasingly being designed to handle multiple channels of fluid, air, or data transfer simultaneously. These multi-channel configurations provide greater versatility and efficiency in various industrial applications.
- Simultaneous Transfer of Fluids, Air, or Data: One of the key advantages of multi-channel rotary joints is their ability to transfer multiple types of media at the same time. Grand’s Fiber Optic Rotary Joints, for instance, can simultaneously transfer fluids, electrical signals, and fiber optic data. This is particularly useful in hybrid systems where data communication, fluid transfer, and air circulation are required simultaneously. The ability to combine multiple functions in a single rotary joint reduces the complexity of systems, minimizes the number of required components, and enhances overall system efficiency. These multi-channel rotary joints are commonly used in applications such as automated manufacturing systems, aerospace, and offshore energy production, where compact, reliable, and efficient solutions are necessary.
Seawater-resistant rotary joints are essential components for industries operating in marine, subsea, and offshore environments. With advanced material selection, leak-proof designs, and multi-channel capabilities, these rotary joints are built to withstand the harshest conditions while ensuring reliable performance and extended lifespans. By using high-quality materials such as 316-grade stainless steel, incorporating advanced sealing technologies, and enabling multi-channel fluid and data transfer, these rotary joints provide the durability and functionality needed to operate safely and efficiently in corrosive environments. Whether for military, aerospace, offshore energy, or chemical processing industries, these rotary joints play a vital role in maintaining operational integrity in challenging environments.
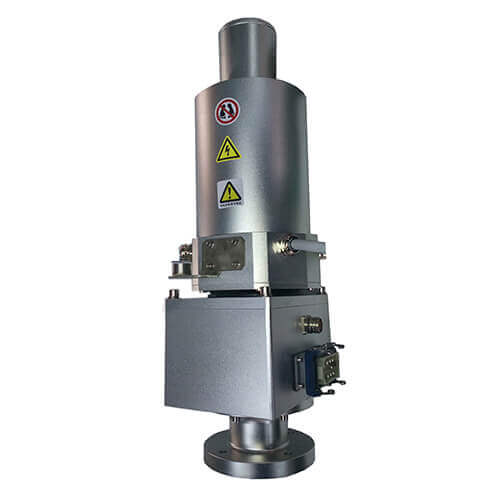

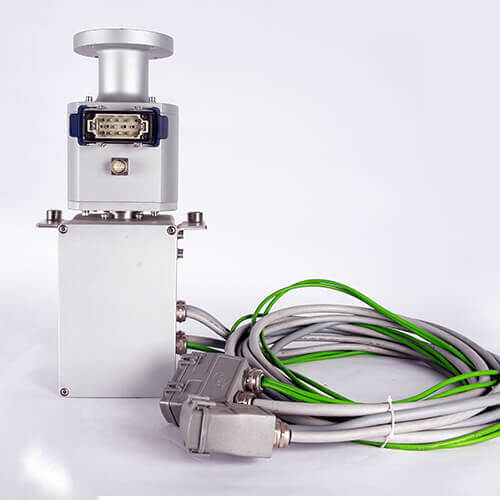
Maintenance and Longevity Tips for Seawater Corrosion Resistant Rotary Joints
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of rotary joints, especially in challenging environments such as marine, offshore, and industrial applications. Regular maintenance not only helps extend the life of the equipment but also ensures its reliability under harsh conditions. Below are key tips for maintaining rotary joints, particularly in environments where corrosion is a concern.
Regular Cleaning to Prevent Salt Buildup
Salt buildup, especially in marine environments, can have a severe impact on rotary joints, causing corrosion and eventually leading to failure if not properly managed. Over time, salt deposits accumulate on exposed surfaces, leading to pitting, rust, and damage to seals and other components.
Best Practices for Stainless Steel Maintenance:
- Wash and Rinse Regularly: After exposure to seawater or saline environments, it’s important to rinse the rotary joint with fresh water to remove salt residues. This should be done after every operation in marine environments to prevent salt from accumulating.
- Use Mild Cleaning Solutions: For thorough cleaning, use a mild detergent or cleaning solution designed for stainless steel. Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive materials, which can damage the surface or seals.
- Dry and Lubricate: After cleaning, ensure the rotary joint is thoroughly dried to prevent any residual moisture from contributing to corrosion. Lubricating the moving parts can also help reduce wear and tear.
Grand’s Solution:
- Grand Slip Rings uses 316-grade stainless steel, which is highly resistant to corrosion. However, regular cleaning is still crucial to maintain its integrity. Adopting routine cleaning practices ensures that saltwater does not compromise the longevity of the rotary joints.
Seal Inspections and Replacements
The seals in rotary joints are critical to their performance. Seals prevent leakage of fluids and maintain pressure within the system. Over time, seals can wear out due to exposure to fluids, heat, or mechanical stress, especially in high-pressure or corrosive environments.
Inspection Tips:
- Inspect Seals Regularly: During routine maintenance, inspect seals for signs of wear or damage. Look for cracks, discoloration, or deformation, as these are indicators that the seals may need to be replaced.
- Monitor for Leaks: Leaking fluid is a clear sign that the seals are no longer functioning properly. If you notice any leakage, inspect the seals immediately and replace them if necessary.
- Check for Contamination: Ensure that no contaminants have built up around the seals, which could hinder their performance.
Grand’s Solution:
- Grand Slip Rings’ rotary joints are designed with easily replaceable seals, making maintenance straightforward. Their modular designs allow for quick service and part replacement, which reduces downtime and ensures reliable operation even in harsh conditions.
Lubrication and Adjustment
Proper lubrication is crucial to maintaining the smooth operation of rotary joints. Lack of lubrication can lead to excessive friction, which in turn can cause wear, overheating, and damage to internal components.
Lubrication Tips:
- Use the Correct Lubricant: Always use the recommended lubricant for your specific rotary joint. The choice of lubricant depends on factors like temperature, pressure, and the type of fluid being transferred.
- Check Lubricant Levels Regularly: Ensure that lubricant levels are adequate. Low levels of lubricant can lead to excessive wear and overheating.
- Avoid Over-lubrication: Excessive lubrication can attract dirt and contaminants, which may interfere with the joint’s operation.
Grand’s Solution:
- Grand Slip Rings’ designs are optimized for minimal friction and extended service life, reducing the need for frequent lubrication. However, ensuring proper lubrication at intervals as per the manufacturer’s guidelines will maximize the performance and longevity of the rotary joints.
Grand Slip Rings stands out as a leader in providing high-quality, corrosion-resistant rotary joints designed for demanding environments. Here are key reasons why Grand Slip Rings is the preferred choice for industries requiring durability and performance under extreme conditions.
1. Expertise in Corrosion-Resistant Materials and Hybrid Systems
Grand Slip Rings specializes in creating rotary joints using 316-grade stainless steel and other advanced materials that offer superior corrosion resistance. These materials are ideal for marine, offshore, and industrial applications where exposure to harsh elements like seawater and high temperatures is a constant concern. Grand Slip Rings’ products are built to withstand the test of time, even in the most aggressive environments.
Moreover, Grand Slip Rings offers hybrid systems, such as multi-channel rotary joints that can simultaneously transfer fluids, gases, and data, making them suitable for advanced systems used in subsea, offshore energy, and aerospace applications.
2. Custom Solutions for Extreme Environments
Grand Slip Rings excels at providing customizable solutions for industries with unique needs. Whether you require multi-channel rotary joints for complex data and fluid transfer, or high-pressure hydraulic rotary joints for heavy-duty operations, Grand Slip Rings offers tailored products designed to meet the specific requirements of your system. The company’s expert engineering team works closely with clients to design and build rotary joints that ensure peak performance, durability, and reliability.
With features such as easily replaceable seals, advanced sealing technology, and corrosion-resistant materials, Grand Slip Rings ensures that their rotary joints not only perform optimally in extreme conditions but also offer easy maintenance and long-term reliability.
FAQs about Seawater Corrosion-Resistant Rotary Joints
Q: What steel resists seawater corrosion?
Seawater corrosion is a significant issue for metals used in marine environments, particularly for steel. While most steels are vulnerable to rust and corrosion when exposed to seawater, some steels are specifically designed to resist corrosion and maintain their strength in such conditions. The most common types of steel that exhibit high resistance to seawater corrosion are stainless steel, particularly the austenitic grades, and specialized alloys.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is one of the most corrosion-resistant materials available. The key to its resistance lies in the chromium content, which forms a passive oxide layer that protects the steel from further corrosion. The higher the chromium content, the better the corrosion resistance. The most common grades of stainless steel used in marine environments are:
- 304 Stainless Steel: Contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel, making it resistant to a wide range of corrosive environments, including seawater. However, it may not be the best choice for long-term exposure to saltwater because of its potential to corrode over time.
- 316 Stainless Steel: Known for its superior resistance to corrosion, 316 stainless steel contains 16-18% chromium, 10-14% nickel, and 2-3% molybdenum. The molybdenum improves the steel’s ability to resist corrosion from chlorides and other aggressive chemicals found in seawater, making it an ideal material for marine environments, boat components, and offshore structures.
- Other Austenitic Steels: Certain special grades like 904L and high-alloyed stainless steels, with higher nickel, chromium, and molybdenum content, offer even better resistance to corrosion from seawater, particularly in highly corrosive conditions.
Duplex Stainless Steel: Duplex steels, such as 2205, offer a combination of austenitic and ferritic structures, which provides higher strength and corrosion resistance than standard austenitic grades like 304 and 316. These steels are particularly effective in seawater applications where both strength and resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking are required.
Superalloys: In extremely demanding environments, such as deep-sea or underwater applications, superalloys made with nickel and molybdenum-based alloys can offer superior corrosion resistance to seawater. These alloys are often used in marine propulsion systems and offshore platforms.
In conclusion, the most seawater-resistant steel is 316 stainless steel, although duplex stainless steels and superalloys can also provide excellent corrosion resistance in harsher environments.
Q: How Does a Rotary Union Work?
A rotary union, also known as a rotary joint, is a mechanical device used to transfer fluids, gases, or other media between a stationary system and a rotating one. This essential component is widely used in applications such as hydraulic systems, rotating equipment, cooling systems, and machinery that require fluid or gas transfer during motion. Rotary unions allow the passage of fluids, such as oil, water, or steam, without causing wear or damage due to rotational movement.
Here’s how a rotary union works:
Basic Structure: The rotary union consists of two main parts: the stationary part, which is connected to the inlet supply (fluid or gas source), and the rotating part, which connects to the rotating equipment or machinery. Between these two parts, there is a seal that allows the fluid or gas to pass while preventing leakage.
Rotational Motion and Seal: The rotating element is typically connected to a shaft or rotating drum, and as the rotating part turns, the fluid or gas flows from the stationary part into the rotating component. To prevent leakage, the rotary union uses seals that are specifically designed to withstand the rotational motion while maintaining a secure barrier between the two parts. Common seal types include mechanical seals, carbon-based seals, and elastomeric seals. These seals allow the fluid to flow seamlessly without escaping or causing friction.
Types of Rotary Unions: There are different types of rotary unions depending on the type of media being transferred and the complexity of the application:
- Single-Passage Rotary Unions: These are designed for a single fluid or gas medium to flow from the stationary to the rotating component. They are simple and efficient for basic applications.
- Multi-Passage Rotary Unions: These unions can transfer multiple fluids or gases at the same time. For example, in a manufacturing process that requires several different fluids (such as oil, water, and air), a multi-passage rotary union allows for simultaneous delivery of all required media.
- Steam Rotary Unions: Specifically designed for high-temperature steam applications, these unions are built with heat-resistant materials to handle the extreme conditions of steam systems.
Applications: Rotary unions are critical in industries such as manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and energy. They are often used in systems like rotary tables, industrial cooling systems, wind turbines, and offshore equipment. In these applications, they ensure that essential fluids (e.g., cooling liquids, hydraulic oils, or lubricants) are delivered to moving components without interruptions, preventing overheating and maintaining machinery efficiency.
Maintenance and Considerations: While rotary unions are robust, they require regular maintenance to ensure that the seals do not degrade, causing leaks or failure. Factors such as the type of fluid used, the temperature, and the pressure applied will affect the longevity and performance of the rotary union. In some cases, routine inspections and the replacement of seals may be necessary to ensure optimal operation.
A rotary union is a crucial component that allows for the smooth transfer of fluids or gases in rotating systems. It functions by using specialized seals to maintain a secure and efficient flow of media, preventing leakage and ensuring the smooth operation of machinery.