This comprehensive article explores the integration of slip ring applications in industrial turntables, highlighting their critical role in maintaining consistent power and data transfer between stationary and rotating platforms. We will delve into different types of slip rings adapted for such use, key selection criteria tailored for industrial needs, and address common challenges with practical solutions. Additionally, we discuss cutting-edge trends that are shaping the future of slip rings in industrial applications and offer answers to frequently asked questions in this area.
Introduction to Slip Ring Applications in Industrial Turntables
In the realm of industrial automation and assembly, turntables play a crucial role—as central cogwheels—in facilitating smooth, consistent movements that are essential for precision work. A turntable, by definition, is a platform that rotates on a central axis, used to transfer objects between different stages of a production line or to display objects in 360 degrees. These rotating platforms must maintain electrical connectivity to power motors, sensors, and other devices critical to their function. Enter the slip ring, an electromechanical device ingeniously designed to solve the problem of transmitting power and electrical signals to a rotating surface without hindrance.
A slip ring is a circular, metal ring that makes continuous electrical connections with stationary brushes or conductive bands as it turns. This electromechanical union allows for the transfer of power and data signals across a rotational interface. Picture an electrical swivel that grants a rotating body the freedom to twist indefinitely, without winding up or damaging the wires that tether it to the fixed world beyond. In essence, slip rings empower turntables to fulfill their dynamic roles, whether they’re rotating a piece of heavy machinery in an industrial setting or showcasing the latest car model at an auto show.
This article outlines the symbiotic relationship between slip rings and industrial turntables. It aims to elucidate the types, applications, and necessary considerations for choosing and maintaining the correct slip ring system in various industrial contexts. Moreover, it’s an exploration into the subtle art of keeping machines in motion, highlighting the crucial yet often overlooked role that slip rings play in the seamless operations of rotating platforms. From the discrete conductive paths etched within to the composite materials encasing them, slip rings are not just accessories but pivotal players in the world of rotary motion.
Understanding Slip Ring Applications in Industrial Turntables
Industrial turntables are powerhouses of productivity hiding in the plain sight of twisting and turning precision. Whether they’re transferring parts along a production line or helping a robot arm spin with accuracy, turntables form the foundation for countless industrial processes. Their operational philosophy revolves around the nuclear principle of rotation, a kind of movement that follows the path of a circle around an axis located in the middle of the turntable. However, for these platforms to function, a perpetual supply of power is crucial. And that’s where slip rings come into the picture.
The conventional method of powering rotating machinery—by using wires that twist and eventually wind up—is fraught with challenges. Tangling wires can obstruct movement, induce stress on the system, and disrupt the longevity and efficiency of the operation. So, to maintain unabated, free motion, engineers incorporate slip rings into turntables.
The design concept of a slip ring is fairly straightforward. Picture a ring that is made of conductive material, connected to an electrical input. As the ring rotates, stationary brushes or conductive bands, also connected to the power source, maintain constant contact with the ring. This ‘slipping’ mechanism lets power or signals be transferred to the rotating part of the turntable without the wires being twisted or snapped.
However, the actual design execution of a slip ring can be complex. Factors such as load capacity, rotational speed, type, and nature of signals or power to be transmitted all have to be factored into the design. Furthermore, adequate materials must be selected for both the ring and brushes to ensure a suitable lifespan and reliable operation, especially in industrial environments where dust, temperature variations, and other variables could affect performance.
In essence, a slip ring allows power, data, or signal transmission between the static structure of the turntable and the rotating platform—making it an unsung hero in the world of industrial automation. Without slip rings, turntables—and, by extension, many of the assembly lines and production facilities that rely on them—would grind to a halt. Thus, understanding slip ring applications in turntables is key to maximizing efficiency and minimizing downtime in many industrial contexts.
Role of Slip Rings in Industrial Turntables
Turntables in industrial settings act as the dynamic intermediary between various stages of the production line. While these machines need to spin freely and continuously, they also need a consistent power supply or means of transmitting electrical signals to fulfill their operational mandate. That’s where slip rings step in as an indispensable mechanical-electrical mechanism, transferring power and data from stationary structures to the ever-rotating platform.
Foremost, slip rings in industrial turntables provide a non-disruptive interface for transferring electrical power between a stationary component—like a direct power source—and the moving part of the turntable. This enables the free spinning of the turntable while maintaining an uninterrupted power supply. This way, motors can be continuously powered, and any programmed machinery on the rotating platform receives the power it needs to operate without interruption.
Alongside power, slip rings also provide an effective means of transmitting data and signals across the rotating interface. In an era where sensors, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and complex control systems govern industrial operations, quick and reliable data transfer mechanisms are more critical than ever. Slip rings, with their ability to transmit a host of data types—like digital signals, analog signals, or even high-frequency signals—prove to be instrumental in establishing the data flow between the stationary and rotating parts of an industrial turntable. By using dedicated conductive tracks and specialized contact materials, these devices ensure seamless and noise-free communication at all times.
Slip rings also play the role of an enabler when it comes to incorporating automation and robotics into industrial turntables. Robotic arms that need to rotate indefinitely, control mechanisms that require feedback from sensors on the rotating parts, or even inspection cameras that need to spin around an object—all these become possible and efficient with the integration of slip rings.
Therefore, the role of slip rings in industrial turntables extends well beyond that of a power and signal conduit; they are integral components that drive fluidity in movement, efficiency in operation, and precision in control. Without slip rings, achieving the necessary reliability and efficacy in operations would be a considerable challenge, if not impossible, in the realm of industrial automation and assembly processes.
Common Types of Slip Rings in Industrial Turntables
In industrial turntables, slip rings are as varied as the applications they serve, each type uniquely engineered to solve specific power and data transfer challenges. Here, we will explore some common types of slip rings and the unique functionalities they bring to the industrial turntable landscape.
Capsule Slip Rings
These are compact slip rings, perfect for applications where space is at a premium. Capsule slip rings are usually used in smaller turntables where low to moderate signals and power need to pass from a stationary to a rotating platform. Despite their small footprint, they are mightily capable of accommodating a surprising number of circuits, transmitting data, and controlling signals efficiently.
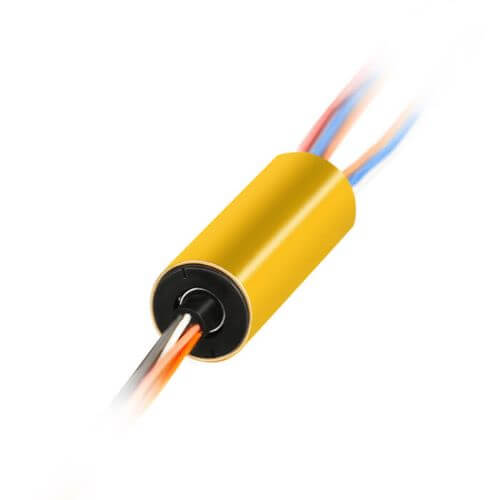

Through-Bore Slip Rings
These slip rings feature a hollow center to accommodate a central shaft or pass-through of other components. The through-bore design is preferred in medium to heavy industrial applications where a larger-scale turntable requires more substantial power transmission capability and a higher number of circuits for control and data.
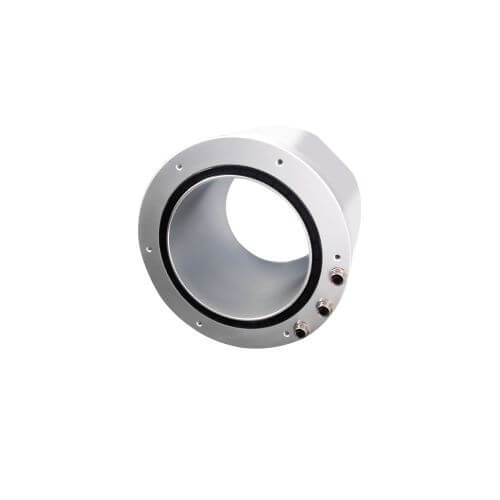

Pancake Slip Rings
Pancake slip rings have a flat, disc-like shape, making them suitable for applications where length is constrained, but there’s sufficient space in diameter. They are chosen for turntables needing a large number of circuits in a relatively flat packaging space.
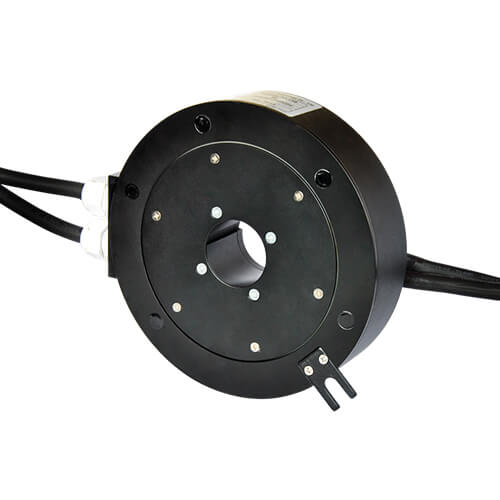

High-Current Slip Rings
When a turntable needs to power heavy machinery, like those found in crane turntables or industrial wind turbines, high-current slip rings are deployed. These are built to handle high power demands, ensuring reliable transmission of substantial currents while the turntable is in motion.
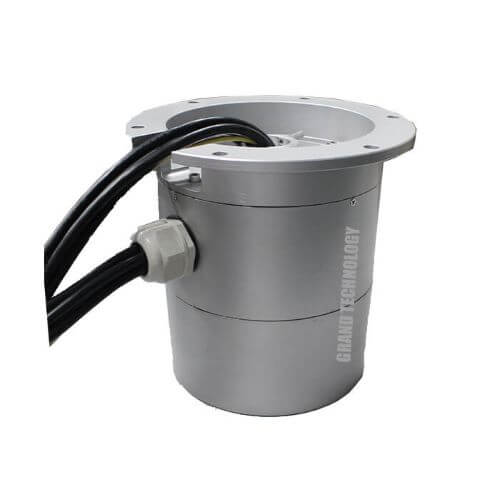

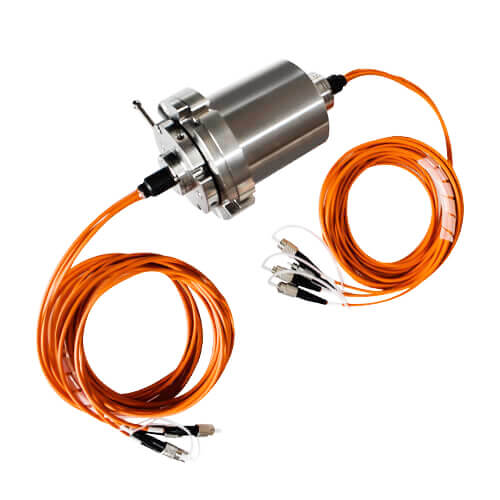
Fiber Optic Slip Rings (FORJs)
For the transmission of high-speed data with minimal signal loss, Fiber Optic Rotary Joints (FORJs) are used. These handle not electrical but optical signals, allowing for uninterrupted high-bandwidth communication which is essential in precise control systems or applications where streaming high-definition video or real-time data is crucial.

Wireless Slip Rings
The rise of wireless technology has also found its place in slip ring development. While not a ‘ring’ in its traditional sense, these devices use electromagnetic fields or induction to transfer power and data, which allows for contactless operation—eliminating friction and wear, resulting in less maintenance and longer life.

Mercury Wetted Slip Rings
These are specialized slip rings that use a pool of liquid mercury to make electrical contact. Their application is niche due to mercury’s conductive properties offering low resistance and thus smooth signal transfer. However, due to health and environmental considerations, their use is limited and highly regulated.

Each type of slip ring caters to a specific requirement of industrial turntables; whether it’s the compactness of capsule slip rings, the current handling capability of high-current slip rings, or the high-speed data transfer achievable through fiber optic units. Selecting the appropriate slip ring type is a critical design decision that impacts the turntable’s functionality, reliability, and overall operational lifespan.
Key Factors in Choosing a Slip Ring for Turntables
Choosing the right slip ring for industrial turntables is no trivial task. It requires a careful evaluation of many interconnected factors to ensure a perfect fit between the needs of the application and the characteristics of the slip ring. Here are some of the key factors to consider when selecting a slip ring:
Environmental Conditions
The environment in which the turntable will operate plays a significant role in slip ring selection. For instance, a slip ring operating outdoors or in damp environments must be weatherproof and rust-resistant. Similarly, slip rings used in industries such as mining or food processing may need to withstand dust, contaminants, high temperatures, or even explosion-proof requirements.
Rotational Speed
Different slip rings are designed to operate at various rotational speeds. It’s essential to choose a slip ring that can handle the rotational speed of the industrial turntable it’s installed on. High-speed applications may need specialized slip rings designed for minimal wear and friction at those high speeds.
Size and Mounting Space
The available space on the turntable affects the type and size of the slip ring that can be used. Capsule slip rings require less space than pancake slip rings, for example. The space available may also dictate the mounting requirements for the slip ring.
Life Expectancy
Different slip ring designs have varying life expectancies. If a turntable is expected to operate for several years without requiring significant maintenance, it may be better to invest in a slip ring with a longer life expectancy, even if it costs more initially.
Maintenance Requirements
Depending on the application, regular maintenance of the slip ring may not be feasible. In such cases, low-maintenance or maintenance-free slip rings, like wireless slip rings, maybe a better option.
Type and Nature of Signals or Power to Be Transmitted
Not all slip rings are alike in their transmission capabilities. Some are designed for transmitting high currents, others for high-speed data transfer, and others still for a combination of power and data. The choice should directly reflect the specific power and data needs of your turntable operation.
Budget Constraints
As with any component, cost plays a role in the choice of a slip ring. It would be best to balance the initial cost of the slip ring with its life expectancy, maintenance requirements, and how well it fulfills your specific needs.
By carefully considering all these factors, one can select the right slip ring that not only meets the needs of the application but also functions reliably over the life of the equipment. Ultimately, the choice of a slip ring can influence the effectiveness, efficiency, and longevity of the industrial turntables and the operations they support.
Slip Ring Applications in Industrial Turntables: Challenges and Solutions
Implementing slip rings in industrial turntables enhances capabilities but also brings unique challenges. Let’s explore some of these issues and potential strategies to mitigate them.
Wear and Tear
By nature, traditional brush and ring slip rings experience inevitable wear and tear due to physical contact and friction. This can lead to the slip ring’s degradation over time, affecting its performance. This is especially true in high-speed applications, where wear rates can be accelerated.
Solution: For applications where wear and tear could become an issue, you may want to consider using contactless alternatives such as wireless or Fiber Optic Rotary Joints (FORJs). Additionally, proper maintenance and regular inspection can help in early detection and repair, prolonging slip ring life.
Signal Interference
Particularly in slip rings transmitting high-frequency data or in environments with a lot of electromagnetic noise, signal interference can be a concern. This could result in data loss or disruption in control signals, impacting the overall system’s operation.
Solution: Careful design of insulation and shielding can reduce electronic interference. High-performance slip rings may also come with specific mitigation strategies, like advanced shielding materials to minimize interference. In some cases, using a Fiber Optic Rotary Joint (FORJ) may be a better choice for transmitting data without electromagnetic interference.
Maintenance Requirements
Traditional slip rings need regular maintenance to avoid damage from debris accumulation between brushes and rings. In addition, cleaning and replacing worn brushes adds to the operational costs.
Solution: To mitigate this, you might consider a sealed or contactless slip ring design that prevents debris build-up and reduces the need for regular maintenance. Wireless slip rings, for example, experience significantly less wear and require less maintenance because they eliminate mechanical contact.
Environmental Conditions
Harsh environments, such as those exposed to dust, moisture, extreme temperatures, or corrosive substances, can shorten a slip ring’s lifespan and decrease its reliability.
Solution: To address this issue, your design may require slip rings made with resistant materials or special sealing. More advanced slip rings may even be housed in a protective enclosure, capable of withstanding these extreme conditions with minimal effect on the device’s performance.
Cost Constraints
High-performance, specialized slip rings can be costly, which can be a prohibiting factor for many applications.
Solution: While cost upfront may be a concern, it’s essential to consider the life-cycle cost, factoring in the cost of maintenance, reliability, and the potential expense of operational downtime due to failures. Sometimes an initially more costly slip ring will be less expensive over its life.
By understanding these challenges and potential solutions, it can be easier to navigate the complex landscape of slip ring applications in industrial turntables. The goal is to ensure the smooth, efficient, and reliable operation of the turntable, hence improving the overall efficiency and effectiveness of your industrial setups.
Slip Ring Applications in Industrial Turntables: Innovative Trends and Future Trajectories
The field of slip ring technology has always been ripe for innovation, continually advancing to meet the ever-evolving needs of industrial applications. As we look into the future, several trends seem poised to significantly enhance the performance, reliability, and longevity of slip rings in industrial turntables.
Advanced Materials
New and advanced materials are being explored to construct slip rings that offer superior conductivity, lower wear, and greater resistance to harsh environmental conditions. For instance, novel alloys and composites can reduce friction, wear, and the effect of thermal expansion, thereby increasing the longevity and reliability of the slip rings.
Contactless Technologies
The trend toward eliminating physical contact between the stationary and rotating parts of the slip ring is becoming increasingly prevalent. Wireless and fiber-optic slip rings are already on the market, presenting solutions to problems like wear and tear, signal interference, and maintenance. As technology progresses, we can expect further improvements in their performance and cost-effectiveness.
Integration of Sensors
The incorporation of sensors directly within slip rings is an emerging trend. These sensors can monitor a range of parameters, such as temperature, speed, vibration, and wear, feeding back real-time information on the slip ring’s operational health. This facilitates preventive maintenance, which can significantly enhance reliability and lifespan.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0
The increased digitalization and automation of industrial applications, also known as Industry 4.0, is impacting the role of slip rings. Higher data transmission rates, improved reliability, and better integration with the networked factory are all becoming more critical. The Internet of Things (IoT) also implies that the slip ring data may become part of a larger data analytics effort to improve overall efficiency and productivity in the factory setting.
Increased Power Transmission
As industrial turntables evolve to support more significant and more complex operations, their power requirements increase. Researchers and manufacturers are continuously seeking ways to safely transmit higher power and more signals without compromising the slip ring’s reliability or life expectancy.
Eco-friendly Alternatives
There is a growing push for sustainable alternatives in all areas of technology, including slip rings. As seen with the move away from mercury-wetted slip rings due to ecological and health concerns, the future might see the adoption of more eco-friendly materials and solutions.
These trends suggest that the future of slip ring technology is very promising. The continuous pursuit of innovation, driven by the manifold requirements of industrial turntables, is likely to spawn cutting-edge slip ring solutions that offer greater reliability, longevity, data integrity, and more. As always, the key will be to match the swiftly progressing technology with the evolving needs of industrial applications.
Conclusion
Wrapping up, we will recap the importance of understanding the necessary role slip rings play within industrial turntables, underscore the key criteria in their selection, and reflect on the potential shifts in slip ring technology that could further benefit this crucial symbiosis.
FAQs about Slip Ring Applications in Industrial Turntables
Below are some of the most commonly asked questions regarding slip ring applications in industrial turntables.
Q1: What is a slip ring?
A: A slip ring is an electromechanical device that allows the transmission of power and electrical signals from a stationary to a rotating structure. It is an essential component in any system where part of the machine needs to rotate continuously, like an industrial turntable, without breaking the electrical connection.
Q2: What types of slip rings are used in industrial turntables?
A: Slip rings used in industrial turntables can be capsule, pancake, through bore, or wireless, depending upon the specific application. The choice significantly depends on environmental conditions, size and mounting space, rotational speed, life expectancy, maintenance requirements, type and nature of signals or power to be transmitted, and budget constraints.
Q3: What are the common challenges faced while using slip rings in industrial turntables?
A: Common challenges include wear and tear, signal interference, the need for regular maintenance, difficulties in adverse environmental conditions, and cost constraints. However, strategies such as using advanced materials, contactless technologies, incorporating sensors, and choosing the right slip ring for your needs can mitigate these challenges.
Q4: What are the maintenance requirements for slip rings in industrial turntables?
A: Conventional slip rings require regular maintenance to prevent damage and ensure efficient operation, including cleaning and occasional brush replacement. However, newer models like wireless, capsule, or sealed slip rings may significantly reduce these maintenance requirements.
Q5: What are the future trends in slip ring technology for industrial turntables?
A: Innovative trends involve the use of advanced materials, contactless technologies, the integration of sensors, compatibility with IoT and Industry 4.0, increased power transmission, and an emphasis on eco-friendly alternatives. These advancements aim to enhance the performance, reliability, longevity, and data integrity of slip rings in industrial turntables.
Q6: How does a slip ring enhance the capabilities of an industrial turntable?
A: Slip rings enable uninterrupted rotation in an industrial turntable while maintaining a constant electrical connection. This ability is crucial for various operations, such as positioning heavy loads, handling materials, or rotary indexing where the machine needs to move continuously or intermittently without breaking the electrical connection.
See What We Can Do

