Welcome to our comprehensive guide on collector rings, a meticulously designed piece to help you fully grasp the world of these vital components within electrical systems. Our guide intends to encapsulate the A to Z of collector rings, from their fundamental roles and extensive applications, right down to their meticulous construction and optimal ways for maintenance.
Acting as something of a compass, this guide will steer you through uncharted waters, enhancing your understanding of what exactly collector rings are and the mechanism behind their operation. Collector rings, often overlooked but incredibly crucial, play a significant role in numerous applications across diverse industries – a testament to their versatility and functionality.
Our endeavor with this guide is no random voyage. It is meticulously curated, aiming to assist both novices and those well-versed with collector rings. For those only starting their journey, this guide serves as an introduction to the fascinating world of electrical system components. For specialists who are already well-acquainted with these gadgets, we provide deeper insights that extend your knowledge further.
No matter what group you fall into, this guide is designed to bolster your comprehension of collector rings, assist you in making informed decisions about your collector ring requirements, and eventually help you optimize the performance and longevity of your applications using these significant components.
Throughout this article, we navigate through each of these areas methodically, revealing the relevance, design, selection criteria, and maintenance protocols of collector rings, offering a unique lens to perceive and understand this essential device. United with our insights and expertise, you’ll sail smoothly through the sea of electrical systems, and collector rings will no longer be chartless territory. So let’s embark on this enlightening journey together, beginning with what collector rings are and why they are so invaluable in the next section.
Definition and Function of Collector Rings
As we move forward in our comprehensive guide on collector rings, it is now time to delve into the heart of the matter by defining what exactly these devices are. To understand their significance, it is vital to get a firm grasp on the fundamentals.
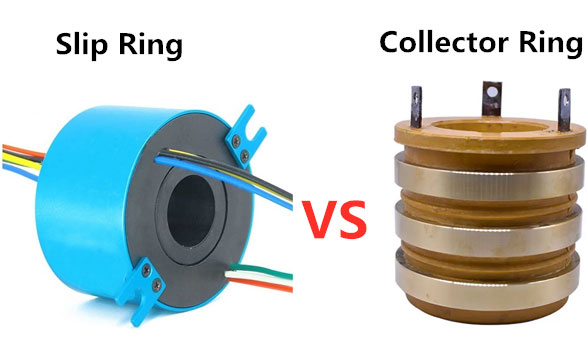
Collector rings, also known as slip rings, form a crucial component within various electrical systems. They can be visualized as an electric nexus, assiduously providing a continuous, stable connection between static and rotating parts. By facilitating unhindered electrical currents or signals, they keep machinery and systems functioning seamlessly, irrespective of whether one part remains constant while the other rotates.
Diving deeper into their functionality, a collector ring broadly comprises two main elements: a ring and a brush. While the ring rotates with the device, the brush maintains a sliding contact with the ring, helping to consistently transfer power or data from the static to the rotating part. Thus, they brilliantly manage to resolve a rather perplexing electrical conundrum — how to maintain electrical continuity throughout motion.
With a professional lens, the utility of collector rings becomes even more apparent. They play an indispensable role in ensuring the uninterrupted operation of many electrical systems. Their ability to provide a reliable connection that stands up to the rigors of movement is paramount in arenas where fluid operation forms the backbone of efficient performance. Through their workings, they conclusively prove that when it comes to electrical systems, movement, and connection are not mutually exclusive.
In essence, collector rings are the unsung heroes in the realm of evolving technology. Though often unseen and largely unnoticed, their heavy-lifting roles in diverse applications testament to their importance. Striking harmony between static and rotating aspects, they have become an essential conduit in the functioning of modern electrical systems. Now, with an understanding of the definition and function of collector rings, the disc of their operation will no longer seem like a mystery.
Design and Construction of Collector Rings
As our deep dive into the complex yet intriguing world of collector rings continues, this segment acquaints you with the design principles and construction details of these devices. Drawing from our extensive industry expertise in designing and manufacturing slip rings, we aim to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of their blueprint and functional elements.
The construction of collector rings is a thoughtful process where each component serves a strategic function. Primarily, a collector ring is composed of two fundamental elements – conductive rings and brushes. The ring is typically mounted onto a rotating shaft while the brush skims along the ring’s surface, leading to a consistent transfer of electrical signals despite the motion.
These components may seem simple at first glance, but the choice of materials and construction design significantly impacts the performance of a collector ring. The conductive rings are typically made of copper or silver alloys, known for their exceptional conductivity. Meanwhile, the brushes can be made of a variety of materials ranging from precious metals to graphite or metallic graphite mixtures. The decision depends on numerous factors like cost, durability, expected operational speed, and many more.
The design choices extend beyond materials. For instance, the amount of pressure exerted by the brush on the conductive ring can substantially influence the durability and efficiency of the system. More substantial pressure can lead to increased electrical capability but could accelerate wear and tear. Moreover, the design may incorporate multiple rings and brushes, allowing the transfer of more than one electrical circuit simultaneously.
Maintenance consideration also contributes to the design choices. Some designs allow for easy brush replacement, while other more compact designs might require specialized maintenance or even a complete replacement after a lifetime of service.
In essence, the design and construction of collector rings are instrumental in determining their overall efficacy, life span, and maintenance needs. With every small design refinement and material choice, these devices are meticulously optimized for the best possible functionality. Holding the spotlight on these intricate details reinforces the adage that, indeed, the devil is in the details. Armed with these insights, understanding the workings of a collector ring becomes a less daunting task and more of a fascinating exploration.
Applications of Collector Rings
As our journey unfolds, it is instrumental to understand the diverse canvas that collector rings paint upon. These seemingly simple devices find their place like pieces of a puzzle in a wide variety of applications—ranging from small consumer electronics to massive industrial machinery.
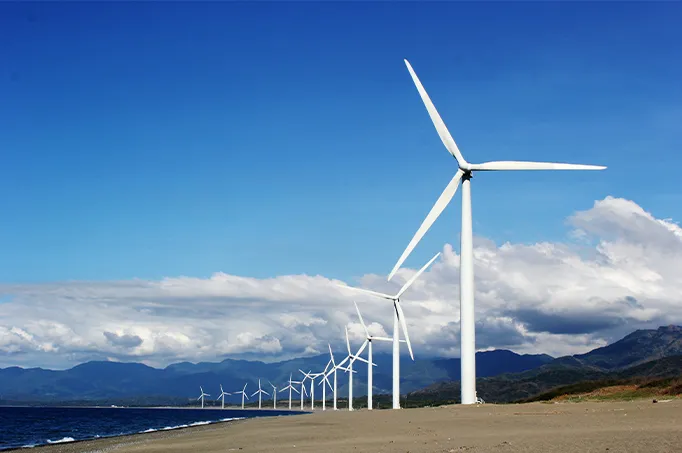
Collector rings play a crucial role in wind turbines, for example. Amid the renewable energy revolution, these humongous structures are ubiquitously found in landscapes all across the globe. In such setups, the turbine’s rotor blades are set in constant motion by the wind. Still, for efficient power generation, an uninterrupted electrical connection needs to be maintained with the static grid. This is precisely the role that collector rings accomplish, thus forming a backbone in the successful operation of wind power generation.

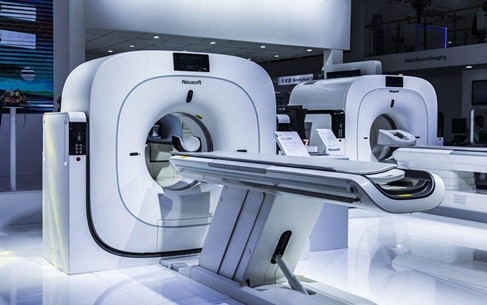
On the other spectrum of size, collector rings also find their significance in the realm of medical imaging devices, such as Computerized Tomography (CT) scanners. In these sophisticated machines, the X-ray source and detectors rotate around the patient at high speeds, producing numerous images from different angles. The challenge here is to ensure a continuous electrical connection for data and power transfer during this rotation, and it is the collector ring that rises to this challenge.
In the industrial sphere, collector rings prove their mettle in an array of applications. Take the case of crane operations, where the crane’s operator cabin needs to rotate to position the load accurately. Here, collector rings ensure the cabin’s rotation while preserving a continuous electrical connection to manage the control signals. They also appear in the broadcasting industry, specifically within rotating antennas, which use collector rings to establish connections while maintaining their ability to rotate for optimal broadcast reception.
Even within the realm of robotics, collector rings fulfill critical roles, enabling rotational movements of robotic arms and joints while maintaining a steady electrical connection. Similarly, they are invaluable in sectors like automotive, communications, and aerospace, always performing the balancing act between motion and connection.

In conclusion, the list of their applications is extensive, demonstrating their widespread value across numerous industries and systems. From colossal wind turbines to precision robotics and everything in between, collector rings serve as the unassuming fulcrum allowing vital systems to function with grace and efficiency. Armed with this new understanding, it becomes clear that these devices are behind many technologies that shape our world.
Advantages and Limitations of Collector Rings
As we navigate further, it is essential to develop a balanced outlook on the capabilities of collector rings. While they carry multiple advantages, it’s equally important to understand their limitations. This understanding of both sides of the coin will empower users to manage expectations effectively and make informed choices tailored to their specific needs.
Advantages of Collector Rings
- Constant Electrical Connectivity: The prominent advantage of collector rings is their ability to maintain a steady electrical connection between stationary and moving parts. This feature eliminates the need for flexible cords which can wear out, tangle, or limit movement.
- Multiple Circuit Transmission: Collector rings can be designed to concurrently transmit multiple electrical circuits, broadening their functionality beyond simple power transfer to encompass various signals like data, video, and control signals.
- Extended Operational Life: Due to their design featuring contact brushes that spread wear across a large surface area, collector rings can have an extended operational life compared to other solutions for managing connections across moving parts.
- Flexibility in Design: Collector rings can be tailored to a wide array of sizes, designs, and materials, allowing them to cater to numerous industrial applications. Their versatility makes them a go-to solution for a range of electrical connectivity challenges.
Limitations of Collector Rings
- Maintenance Requirements: Over time, wear and tear on collector rings can degrade performance. The brushes may need occasional replacement, which implies that appropriate maintenance practices are required to ensure optimal operation.
- Not Ideal for High Frequency: Collector rings might face challenges in transmitting high-frequency signals due to potential signal noise and attenuation caused by the sliding contact design.
- Environmental Concerns: The functioning of collector rings can be influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and dust, thus necessitating protective measures to ensure consistency in performance.
- Space Requirements: Collector rings might require more space than other forms of rotary connectors like rotational transformers, for instance. They may not be the best choice for applications with severe spatial constraints.
Through a clear perception of both the benefits and potential limitations of collector rings, users can make a well-informed decision aligning with the particular preconditions and expectations of their application. As with any technology, the best use of collector rings comes from understanding precisely when and where they excel.
Collector Rings: Selection Criteria
As we embark on the final leg of our comprehensive guide on collector rings, it’s time to delve into the crucial selection criteria when choosing a collector ring. Like fitting a key to a lock, each application has a specific set of requirements and conditions under which the ring will operate. These criteria encompass a diverse range of factors including environmental conditions, power and signal requirements, operational speed, and more.
- Operational Environment: The environment in which the collector ring will function is the first fundamental factor in selection. If the device will operate in harsh conditions, for example, high temperatures, high humidity, or dusty areas, it is prudent to choose a collector ring designed to resist these challenges without compromising performance.
- Power and Signal Requirements: Understanding the power and signal needs of the application is crucial. High-power applications may require larger, more robust collector rings, while sensitive data signals may warrant the use of collector rings specifically designed to minimize noise and interference.
- Operational Speed: The speed of rotation also comes into play. At higher speeds, the collector ring must be able to maintain a secure, reliable connection without excessive wear, which may necessitate the use of specialized materials for the brushes and rings.
- Installation Space: The available physical space for installing the collector ring should also be considered. Compact applications may require the use of collector rings designed with space efficiency in mind, without compromising on performance.
- Maintenance Accessibility: If regular maintenance is going to be a challenge, due to limited accessibility or unavailability of skilled personnel, then collector rings designed for extended use between service intervals, or with easily replaceable components, may be the right choice.
- Budget Constraints: Last but certainly not least, the budget plays an overarching role in the selection process. The objective should be to find a balance between optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Choosing a collector ring, therefore, is a process that goes well beyond a simple parts list. By paying careful attention to these essential selection criteria, users can be confident they are making a solid, well-informed choice. In that way, the chosen collector ring will not only meet the immediate application requirements but also provide longer-term reliability, ensuring smooth, uninterrupted operations.
Collector Rings: Maintenance and Troubleshooting
As with any mechanical or electrical device, proper maintenance and troubleshooting play a key role in the overall lifespan and performance of a collector ring. This section will delve into important aspects of collector ring maintenance, including identification of common issues, essential inspection practices, and when to seek professional assistance.
Periodic Inspections
Performing regular check-ups and visual inspections are the cornerstones of effective maintenance. Key factors to monitor include:
- Brush Wear: Over time, brushes may wear down and lose their ability to maintain proper contact with the conductive ring. Regularly inspecting the brushes for wear and tear and replacing them when necessary ensures a consistent, reliable connection.
- Conductive Ring Surface: Examine the surface of the conductive rings for any uneven wearing or grooves, which could be an indication of excessive brush pressure or other issues. A timely intervention could prolong the ring’s lifespan.
- Location and Clearances: Check the position of the brushes and the clearance between the brush and the conductive ring to ensure proper contact. In case of misalignment or excessive wear on either the brush or the ring, corrective measures must be taken.
- Debris and Contamination: Keep an eye out for any accumulation of dust, debris or contamination around the collector ring, as this may cause signal noise, interference, or premature wear of components. Regular cleaning can mitigate such consequences.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Some common issues observed in collector rings and potential troubleshooting steps are:
- Intermittent Connection: If experiencing an intermittent signal, verify the cleanliness of the brush and conductive ring surfaces, ensuring they are free of dirt, debris or oxidation. Moreover, assess the brush pressure and adjust it if necessary.
- Excessive Noise or Interference: When encountering excessive electrical noise or interference, consider evaluating the shielding of electrical cables and connections, as well as the proper grounding of the collector ring assembly.
- Rapid Wear or Degraded Performance: Rapid wear or degraded performance may be indicative of incorrect brush pressure or the use of incompatible materials for brushes and rings. Consult the manufacturer for recommended brush materials and pressure settings for your specific application.
Seeking Professional Help
While routine maintenance and basic troubleshooting can often be handled by the user, complex issues or significant component damage may warrant professional help. In such instances, contacting the manufacturer or a qualified technician for assistance is the best course of action to ensure the longevity and performance of the collector ring.
In conclusion, proper maintenance and an understanding of troubleshooting practices are vital for maximizing the performance and lifespan of collector rings. By staying attentive to the condition of your collector rings and addressing concerns at their earliest stages, you can help ensure their long-term reliability and effectiveness in your application.
Collector Rings: Future Trends and Technology
Keeping up with industry advancements is vital for the longevity of your application. Modern collector rings are seeing an impact from the increased use of advanced materials for better durability and performance, smart diagnostic systems for enhanced reliability, and modularity for easy replacement and repair.
In conclusion, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge to understand, choose, and maintain collector rings efficiently. By understanding collector rings from a professional perspective, you can ensure that you make the right choices that enhance the performance and lifespan of your applications.
FAQs about Collector Rings
To cater to common queries and help users gain a more in-depth understanding of collector rings, we’ve included this Frequently Asked Questions section. This segment of the guide provides clear and concise answers addressing issues related to the usage, maintenance, potential problems, and overall management of collector rings.
Q: How should I clean my collector ring?
A: Regular cleaning maintains connectivity and longevity. Mild cleaning solutions with non-abrasive cloth can safely clean and deoxidize the ring surfaces. However, use caution not to damage the conductive surface.
Q: Which material should be selected for collector ring brushes?
A: The brush material depends on numerous factors including operating speed, operating environment, signal type, and power requirements. Common materials include brass, graphite, silver-graphite, and more. You should consult with the collector ring manufacturer for an accurate recommendation.
Q: My collector ring seems to heat up during operation. Is this normal?
A: Slight warming is normal. However, excessive heating could indicate an issue such as too much brush pressure or a possible overload condition. This should be professionally inspected to avoid potential damage.
Q: What should I do if signal transmission becomes intermittent?
A: First, check the condition of the brushes and the cleanliness of the conductive ring. Accumulation of debris can be a common cause of connectivity problems. If the problem persists, a professional inspection may be necessary.
Q: Can I use a collector ring in a high-vibration environment?
A: Yes, but note that collector rings in high-vibration settings may require additional support or customization to ensure reliable operation. Specialized materials and designs can help improve their performance under such conditions.
Q: Can a collector ring transmit data as well as power?
A: Yes, collector rings can be designed to handle both power and various data signal types concurrently – including digital, analog, video, and control signals – expanding their utility across diverse applications.


