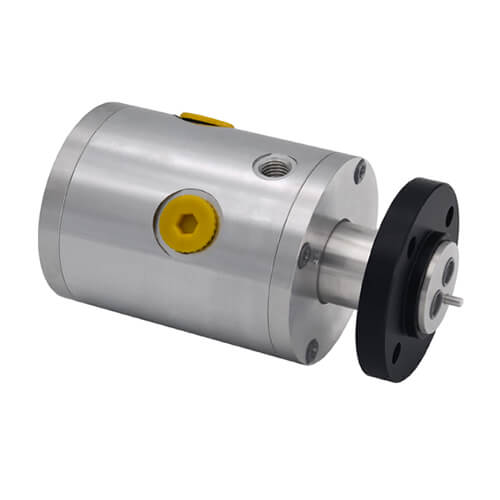
This article serves as an all-inclusive guide, delving into what hydraulic rotating unions are, their operation, application across various industries, guidelines for selection, common issues and their resolution, recent technological advancements, and a look into the future usage of these components. We aim to arm readers with the necessary knowledge for making well-informed decisions regarding hydraulic rotating unions, ensuring efficient and effective utilization in their specific applications.
Introduction to Hydraulic Rotating Unions
A hydraulic rotating union, also known as a rotary union or a swivel joint, is a precisely designed mechanical device used to transfer fluid, typically hydraulic or pneumatic, between rotating and stationary components. Essentially, they are the “conduit” for fluid transfer in a range of machinery where rotation is involved. This means they play a foundational role in the operation of a multitude of systems from industrial operations to commercial utilities and more.
Hydraulic rotating unions have a pivotal role in many industrial applications. They allow the circulation of necessary fluids – such as cooling or heating agents – from a stationary supply line to a rotating piece of machinery. These unions are commonly found in industries including manufacturing and machining, automotive, aerospace, renewable energy, and more.
In manufacturing, for instance, hydraulic rotating unions might facilitate the movement of cutting fluids to a rotating cutting tool to cool down heat generated by the machining process. In the renewable energy sector, hydraulic rotating unions are integral to the functioning of wind turbines, taking the high-pressure hydraulic fluid from the stationary part of the turbine to the rotating blades.
Ultimately, the purpose of hydraulic rotating unions is to maintain a consistent, leak-proof flow of fluid to rotating parts, even in high-speed, high-pressure, or high-temperature conditions. By ensuring a seamless flow of fluids, hydraulic rotating unions contribute significantly to enhancing operational efficiency, extending the lifecycle of equipment, and ensuring the safety of the work environment in a large number of industrial settings.
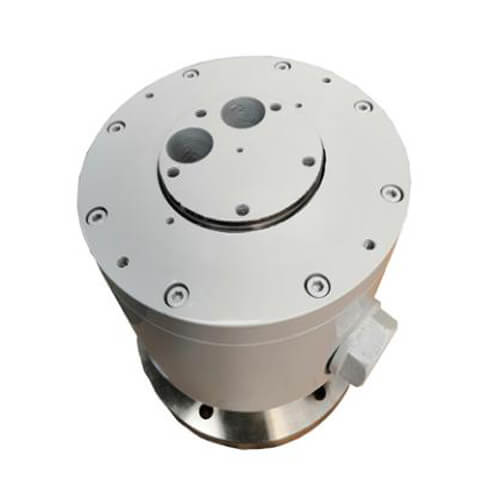

The Basics of Hydraulic Rotating Unions
Hydraulic rotating unions are mechanical devices enabling the transfer of fluid from a stationary source to a rotating part, ensuring continuous flow without any leakage or interruption. The primary function of these unions is critical in applications where fluid needs to be moved into or out of a rotating part, such as in cooling systems, hydraulic circuits, and pneumatic systems. They serve as a bridge, facilitating the seamless operation of complex machinery by allowing the transfer of fluids under various pressures and temperatures while the machinery is in motion.
Core Components
At the heart of every hydraulic rotating union are several key components that ensure its efficient operation and durability:
- Seals: These are perhaps the most critical elements, designed to prevent leakage of the transferred fluid at the connection points between the stationary and rotating parts. The types of seals vary based on the application’s demands, fluid type, pressure, temperature, and rotational speed.
- Shaft: This is the rotating part of the union onto which the seal is placed and against which the seal runs. The shaft’s design and material are pivotal for the union’s longevity and reliability.
- Housing: Provides the structural support for the union and houses the internal components. It is typically designed to withstand the operating pressures and temperatures and is made from materials compatible with the fluid being transferred.
Types of Hydraulic Rotating Unions
Hydraulic rotating unions are categorized into various types, primarily based on design, the media they are intended for, and their specific application needs:
- Design: They can be single-passage or multi-passage. Single-passage unions allow for the transfer of one type of fluid, whereas multi-passage unions permit the simultaneous transfer of multiple fluids or gases through separate channels, accommodating more complex system requirements.
- Media: The type of fluid or gas a union is designed to handle significantly influences its design and the materials used for its components. Common media types include water, oil, and air, each requiring different seal materials and designs to ensure efficient and reliable operation.
- Application Specificity: Hydraulic rotating unions are also categorized based on their specific applications, such as cooling or heating processes. For example, cooling unions may be designed to handle lower temperatures and specific flow rates suitable for removing excess heat from equipment, whereas heating unions may be designed to withstand higher temperatures associated with heating processes.
Understanding these basic components and distinctions is crucial when selecting the right hydraulic rotating union for a specific application, ensuring that the union can meet the operation’s requirements in terms of fluid type, pressure, speed, temperature, and reliability.
Hydraulic Rotating Union Operating Principles
The operational functionality of hydraulic rotating unions is a marvel of mechanical engineering, designed to solve the complex challenge of transferring fluids between stationary and rotating parts without leakage. At its core, the operation of hydraulic rotating unions is governed by a few fundamental principles that ensure seamless and efficient fluid transfer, preserving the integrity and performance of both the fluid and the machinery involved.
Explanation of How Hydraulic Rotating Unions Work
Hydraulic rotating unions function by establishing a mechanical linkage that seals and maintains a continuous conduit for fluid flow between fixed and moving parts. The union typically consists of a stationary input (often referred to as the housing) and a rotating output (the shaft), which is connected to the part of the machinery that rotates. The fluid enters the union through the stationary side, where it is then guided through precision-engineered channels within the union to reach the rotating part.
Central to this process is the seals within the union, which are meticulously designed to ensure that fluid does not escape the system, particularly at the point where the stationary and rotating parts meet. These seals must accommodate the relative movement of the rotating parts while maintaining a tight seal under the operational pressures and temperatures specific to the application. The effectiveness of these seals, in conjunction with the structural integrity of the shaft and housing, determines the efficiency of the fluid transfer and the overall reliability of the rotating union.
Role in Transferring Fluids Between Stationary and Rotating Parts
The primary role of hydraulic rotating unions is to facilitate the uninterrupted transfer of fluids between stationary and rotating parts, a requirement common in a vast array of industrial applications. This ability is particularly valuable in machinery and systems where lubrication, cooling, or the transfer of hydraulic power is necessary for the rotating part to function effectively.
In industrial machining, for example, hydraulic rotating unions are used to transport cutting fluids to the site of cutting, providing necessary lubrication and cooling directly to the rotating cutting tools. In the realm of thermal management, rotating unions enable the circulation of heat transfer fluids through rotating drums or rolls, critical for processes such as paper drying or plastic film extrusion. Similarly, in hydraulic systems, they are essential for conveying hydraulic fluid to actuate rotating mechanisms without hindrance.
By allowing for the direct transfer of fluids into moving parts without the need for hoses or tubes that could bend, twist, or break under the stress of rotation, hydraulic rotating unions significantly enhance the functionality, efficiency, and safety of industrial equipment. They enable complex machinery to operate smoothly and continuously, minimizing downtime, maintenance requirements, and operational costs, while maximizing the machinery’s productivity and lifespan.
Hydraulic rotary joints, also known as hydraulic rotating unions, are essential components in the efficient operation of next-gen excavators. These joints enable the continuous transmission of hydraulic fluid and electrical signals between stationary and rotating parts, eliminating the need for separate systems. By providing a compact solution that handles both fluid and electrical transfers simultaneously, hydraulic rotary joints enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of modern machinery.
Hangzhou Grand Technology’s Contribution
Hangzhou Grand Technology has advanced this field with its electro-hydraulic combined rotary joints. These rotary joints provide a solution to the limitations of traditional electric slip rings, which could only transmit electrical power. Grand Technology’s innovations allow for the simultaneous transmission of hydraulic fluids (such as oil or coolant) and electrical signals. This dual functionality is essential for the modern design of excavators, as it ensures the continuous flow of both power and fluid without interruption, improving reliability and efficiency.
In Servoday’s project to convert traditional excavators to electric-powered systems, hydraulic rotary joints played a crucial role. By integrating Grand Technology’s electro-hydraulic combined rotary joints, Servoday was able to create an efficient system where both hydraulic operations and electrical controls could be managed simultaneously.
This integration significantly boosted the performance of the electric excavator. The hydraulic rotary joints allowed for seamless operation of hydraulic arms, cooling systems, and electrical signals without interference. This reduced the number of components needed, simplifying the design and lowering maintenance costs. The system also ensured that data transmission and fluid management could work together smoothly, providing operators with better control and reducing the risk of mechanical failures.
Hydraulic Rotating Union Key Applications and Industries
The indispensable nature of hydraulic rotating unions spans a broad range of industries, each relying on these components for critical operational functions. From manufacturing and machining to automotive, aerospace, oil & gas, and the fast-growing sector of renewable energy, hydraulic rotating unions play a pivotal role in ensuring efficiency, safety, and reliability.
Manufacturing and Machining
In the realm of manufacturing and machining, hydraulic rotating unions are integral to the operation of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines. These machines perform highly precise cutting, drilling, and milling tasks on various materials. Hydraulic rotating unions facilitate the transfer of cutting fluids directly to the cutting head or spindle, ensuring effective cooling, lubrication, and removal of metal shavings, thereby extending tool life and improving product finish.
Automotive
Within the automotive industry, these unions find their application in the automation of production lines. They are used in robotic arms for tasks that require rotation, like welding or assembly, where they manage the flow of power, data, and fluids necessary for the operation. They also play a critical role in test benches for engines and transmissions, where they supply the necessary fluids under controlled conditions, simulating various operational environments.
Aerospace
The aerospace sector demands the utmost precision and reliability, given the high-stakes nature of its products. Hydraulic rotating unions are employed in the manufacturing processes of aircraft components, providing essential fluids to cool and lubricate parts during high-speed machining. Furthermore, they are fundamental in the testing stages of engines and hydraulic systems, ensuring these critical components can withstand the rigors of flight.

Oil & Gas
In the oil & gas industry, hydraulic rotating unions are used in drilling equipment, facilitating the transfer of drilling mud to lubricate and cool drill bits while flushing out cuttings from the wellbore. This not only enhances drilling efficiency but also contributes significantly to the safety and environmental compliance of drilling operations.
Renewable Energy
The renewable energy sector, particularly wind power, has seen an increased integration of hydraulic rotating unions. They are critical in wind turbines for hydraulic pitch control systems, which adjust the angle of the blades to maximize efficiency and protect the turbine in high winds. These unions provide a continuous flow of hydraulic fluid, ensuring smooth and responsive control of the blades.

Specific Application Examples
In CNC machines, hydraulic rotating unions are essential for their high-precision cooling systems. They allow coolants to be applied directly to the cutting edge, preventing overheating and thermal distortion of the workpiece and tool.
In automotive cooling systems, these unions are used within dynamic test benches, allowing for the simulation of real-world conditions by controlling the flow and temperature of coolant through the engine, transmission, or other components under test.
In the wind energy sector, hydraulic rotating unions play a critical role in the hydraulic pitch control systems of wind turbines. By facilitating the transfer of hydraulic fluids, they enable precise control over the blade pitch, optimizing the turbine’s performance across a wide range of wind conditions while ensuring its safety during operational extremes.
Across these diverse applications and industries, the fundamental function of hydraulic rotating unions—transferring fluids in a leak-proof manner between stationary and rotating systems—remains constant. This function is critical to the operation, efficiency, and safety of the machinery and processes in which they are employed, underlining the broad utility and importance of hydraulic rotating unions in modern industry.
Selection Criteria for Hydraulic Rotating Unions
Choosing the right hydraulic rotating union for an application requires careful consideration of a range of factors to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and hence the operational efficiency of the related machinery. Key factors include media type, pressure and flow requirements, speed, and temperature constraints, and size and connection standards.
Media Type and Compatibility
Crucial to the selection of a hydraulic rotating union is the consideration of the type of medium to be transferred — this could be air, water, hydraulic oil, or other specialized fluids. The selection must account for compatibility with both the seals and the materials of the union itself, to prevent leakage, corrosion, and degradation over time.
Pressure and Flow Requirements
Just as important are the pressure and flow requirements of the application. These determine the size and design of the channels within the union and the strength of the materials used. High-pressure applications require more robust seals and heavier construction to withstand extreme forces, whereas high-flow applications may necessitate larger or multiple channels within the union to facilitate the necessary volume of fluid.
Speed and Temperature Constraints
Speed and temperature conditions are fundamental considerations. High rotational speeds can generate significant heat and may necessitate the use of specialized materials to prevent premature wear and operational failure. At the same time, the temperature of the transferred media and ambient conditions can influence the types of materials and seals suitable for use in the application.
Size and Connection Standards
Size constraints and connection standards are also essential selection elements. The rotating union needs to physically fit into the designated space in the machinery, and its connections must match the corresponding interfaces for seamless integration. Therefore, considering the compatibility with relevant national or international standards like ANSI, ISO, or JIS is vital to ensure the unions can be connected without requiring additional adapters or modifications.
Importance of Customization and Compatibility with Specific Machinery
Given the wide variety of applications and the specific needs of different machinery, customization plays a key role in hydraulic rotating union selection. Some applications may require custom-designed unions, tailored for specific media, ranges of pressure, speed, temperature, and precise fitting and connection standards.
Customization ensures not only the compatibility of the union with the machinery but also optimizes its performance and efficiency within the specific operational environment. Without proper customization, the machinery could experience inefficiencies, potential operational failures, increased maintenance needs, and diminished lifespan.
In conclusion, choosing the correct hydraulic rotating union encompasses a careful assessment of both the operation’s specific requirements and the broader operational environment. These considerations help to ensure the selected union can reliably perform its function over its intended lifespan, thereby optimizing the machinery’s functionality, efficiency, and longevity.
Hydraulic Rotating Union Common Issues and Maintenance Tips
Hydraulic rotating unions, while designed for high performance and durability, are not immune to complications and wear over time. Common issues such as leakage, excessive wear, and tear, or operational performance degradation can occur under certain conditions. However, with a proactive approach towards maintenance and a general understanding of troubleshooting, the lifespan and efficiency of these rotating unions can be significantly improved.
Common Problems Faced by Users
- Leakage: Consequent to improper seal or seal wear, leakage is a common issue in hydraulic rotating unions. Not only does this result in fluid loss, but leaking fluid can contaminate the surrounding environment and potentially damage other components of the machinery.
- Wear and Tear: Over time, moving parts of the union, particularly the seals and the surfaces they interact with, can wear down. This wear can degrade the union’s performance, causing leakage, inefficient fluid transfer, or even complete failure of the union.
- Performance Degradation: Without regular maintenance and inspection, components can degrade, leading to deteriorating performance over time. This might result in lower fluid flow rates, unexpected pressure drops, and other reductions in operational efficiency.
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Preventive maintenance strategies can help reduce the occurrence of these common issues and prolong the lifespan of a hydraulic rotating union.
- Regular Inspections: Regular visual inspections can help detect issues like leakage or unusual wear early. Look for signs of fluid around the union or wear on the exposed rotating shaft.
- Scheduled Seal Replacements: Seals have finite service lives, even under the best conditions. Proactive replacement of seals according to a maintenance schedule can prevent sudden failures or leaks.
- Clean Fluids: Ensuring the cleanliness of the fluid used in the union can prevent premature wear and tear or blockage in the fluid channels.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If problems arise despite preventive measures, troubleshooting may help to identify and resolve the issue.
- Investigate Leaks: If fluid is found around the union, investigate the source of the leak. It might be the seal, a crack in the housing, or a loose connection, each requiring different solutions.
- Observe Function: If the union’s performance drops, observe its operation. A union rotating with difficulty could signal an issue with the bearing, which might need replacement.
- Confirm Specifications: If issues persist, confirm that the union matches the specifications required for the application. A mismatch in factors such as fluid type, pressure capacity, or rotational speed can cause ongoing issues.
Understanding the operation of hydraulic rotating unions, along with common problems and maintenance strategies, will optimize the performance, reliability, and service life of these critical components. Regular inspections, preventive maintenance, and troubleshooting of unexpected problems are key parts of keeping rotating unions—and the machinery they serve—operating smoothly and efficiently.
Hydraulic Rotating Union Innovations and Future Trends
In the realm of fluid power and motion control, hydraulic rotating unions have seen substantial technological advancements. These innovations aim to enhance performance, reduce maintenance costs, and increase the lifespan of these components. Looking forward, we can anticipate the burgeoning integration of these unions with smart technologies and their application in new and expanding markets.
Latest Advancements in Hydraulic Rotating Union Technology
- Improvements in Seal Materials
Advances in material science have led to significant improvements in seal materials for hydraulic rotating unions. Modern seals are made of proprietary composites that offer better wear resistance, longer life, and improved resistance to the high-temperature and aggressive chemicals they might encounter. Materials like polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) composites, various elastomers, and advanced ceramics, are being engineered to provide optimal sealing properties even under fluctuating pressures and speeds. - Integration with IoT for Predictive Maintenance
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology into hydraulic rotating unions represents a forward leap in monitoring and maintenance strategies. Sensors can be embedded directly into components to constantly transmit data concerning operational parameters such as pressure, temperature, and rotational speed to centralized control systems. This real-time data collection supports predictive maintenance programs, whereby maintenance needs can be anticipated and addressed before failures occur, dramatically reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Potential Future Applications and Market Growth Trends
The horizon for hydraulic rotating unions is broadened by emerging applications in various fields, which promise to drive market expansion.
- Renewable Energy Sector Developments
As the global focus on renewable energy intensifies, hydraulic rotating unions will likely see increased demand in applications such as solar power concentrators and wind turbine pitch and yaw control systems. These unions’ ability to reliably function in variable environmental conditions makes them well-suited for such demanding applications. - Advanced Robotics and Automation
Automation and robotics continue to push into new domains, from manufacturing to service industries. Increased complexity and functionality in these fields necessitate the use of hydraulic systems for precision control, where hydraulic rotating unions will be vital for the continuous delivery of power and fluids. - Aerospace and Deep-Sea Exploration
The aerospace industry’s push for more effective cooling systems in aircraft and spacecraft may see higher usage of advanced hydraulic unions. Similarly, as deep-sea exploration ventures further and the equipment it requires becomes ever more sophisticated, hydraulic rotating unions capable of withstanding high pressures and corrosive environments will be essential.
In summation, future trends for hydraulic rotating unions point to their integration with more advanced materials and smart technologies. This convergence of technology not only propels the functionality and practicality of hydraulic rotating unions forward but also heralds their expansion into new and innovative applications. The promise of increased operational efficiency and reduced maintenance, combined with expanding markets, underscores the enduring importance of these versatile components.
Making an Informed Decision on Hydraulic Rotating Unions
Selecting hydraulic rotating unions requires thoughtful consideration. These crucial components serve as indispensable elements in various applications and industries. Nevertheless, the meticulous selection process doesn’t end with understanding the union’s specifications and operational requirements. Factors such as the manufacturer’s reputation, the level of technical support, and the quality of after-sales service play pivotal roles in the overall decision-making process.
Importance of Working with Reputable Manufacturers
Choosing to work with a reputable manufacturer is an integral part of the decision-making process. Renowned manufacturers have earned their reputation due to their commitment to quality, innovation, and customer service.
- Quality Assurance: Esteemed manufacturers use high-quality materials and apply stringent manufacturing standards, crucial for the product’s performance and durability. The products they deliver are often more resistant to operational wear and tear, displaying longer service life.
- Cutting-edge Innovation: Reputable manufacturers invest heavily in research and development. Thus, their products are more likely to incorporate the latest advancements and improvements that might enhance efficiency, ease of use, and operational lifespan.
- Reliability: With their reputation at stake, these manufacturers are less likely to compromise on the integrity of their products, reducing the risk of product failures that can lead to costly downtime.
The Role of Technical Support and After-Sales Service
Beyond choosing quality products, strong technical support and robust after-sales service offer essential value.
- Technical Support: Manufacturers providing excellent technical support can help you select the right product to meet your specific needs, offer assistance during the installation process, and provide valuable guidance if operational issues arise.
- After-Sales Service: A robust after-sales service includes access to spare parts, regular maintenance and inspection services, and quick and efficient repair services. This support can significantly enhance product lifespan and operational efficiency, and it ensures that any disruptions to your operations are minimized.
Final Thoughts on Optimizing the Selection Process
The decision-making journey doesn’t end with understanding the operational requirements and choosing a hydraulic rotating union that meets these needs. The selection process is multi-faceted and requires significant considerations beyond the product specifications.
- Value for money: Making an informed decision is about more than finding the cheapest product. It’s about finding the product that will offer the best performance, lifespan, and reliability for your operational needs—qualities that offer real long-term value and can save you money in the long run.
- Understanding your needs: Different operations will have different needs, and understanding these needs thoroughly is key to making the best decision.
- Looking beyond the product: The quality of the manufacturer and the level of support they can provide are nearly as important as the product itself. Ensuring that you can rely on your supplier can make all the difference in your operation’s success.
In conclusion, the process of selecting a hydraulic rotating union is about making an informed decision, taking all relevant aspects into account—from the specifications of the product itself to the reputation and reliability of the manufacturer. By paying attention to these diverse elements, you will ensure that you are choosing the best product for your needs and securing your operations’ optimal efficiency and longevity.
Conclusion
Understanding the varied roles of hydraulic rotating unions in industry highlights their importance. As technological advancements continue, their applications may broaden – emphasizing the need for informed decision-making from application to maintenance for efficient use.
FAQs about Hydraulic Rotating Union
Q: What is a hydraulic rotating union?
A: A hydraulic rotating union is a mechanical device that allows the transfer of pressurized fluids from a stationary system to a rotating structure without leakage.
Q: How do I choose the right hydraulic rotating union?
A: When selecting a hydraulic rotating union, consider media type, pressure requirements, speed, temperature constraints, size, and compatibility with existing systems.
Q: What are some common issues with hydraulic rotating unions?
A: Some frequent problems include leakage, accelerated seal wear, and overall mechanical wear due to improper selection or lack of maintenance.
Q: Can hydraulic rotating unions be customized for specific applications?
A: Yes, many manufacturers offer customized hydraulic rotating unions to meet the precise requirements of a particular application or industry.
Q: How are technological advancements affecting hydraulic rotating unions?
A: Advancements in material science and IoT integration are leading to longer-lasting seals and predictive maintenance capabilities, which improve the overall efficiency and reliability of hydraulic rotating unions.
Q: What exactly is a hydraulic rotating union?
A: A hydraulic rotating union is a mechanical device designed to transfer fluid from a stationary source, such as a pipe, to a rotating part, such as a drum, cylinder, or spindle. It enables the flow of hydraulic fluid, water, or other media while allowing the connected part to rotate freely without the risk of tangling or kinking hoses.
Q: How do I know which hydraulic rotating union is right for my application?
A: The right hydraulic rotating union depends on various factors such as the medium being transferred, pressure and flow requirements, speed of rotation, temperature, and the environment in which it will operate. Consulting with technical experts and providing detailed operational requirements will ensure you select a union that meets your specific needs.
Q: Can hydraulic rotating unions be repaired, or do they have to be replaced when they malfunction?
A: Many hydraulic rotating unions can be repaired, depending on the nature of the malfunction. Seal kits and replacement parts are often available for common models. However, some damages or malfunctions may be so severe that they necessitate a complete replacement. Consulting with the manufacturer is the best course of action when a malfunction occurs.
Q: What is the typical lifespan of a hydraulic rotating union?
A: The lifespan of a hydraulic rotating union can vary widely depending on its usage conditions, the quality of the seals and materials used in construction, and how well it is maintained. Regular maintenance and proper installation can help extend the life expectancy significantly. Some can last for many years, even in demanding conditions.
Q: Are there any recent innovations in hydraulic rotating union technology I should be aware of?
A: Recent innovations include the development of more durable seal materials and the integration of smart technology, which allows for predictive maintenance through IoT. These advancements help to reduce downtime, increase efficiency, and prolong the lifespan of the unions. Always check with manufacturers for the latest in their product lines.
Q: Is it important to use a filter with a hydraulic rotating union?
A: Yes, using a filter is highly recommended to remove contaminants from the fluid, which can cause premature wear and tear on the seals and internal parts of the rotating union. Clean fluid is essential for the longevity and optimal performance of the union.
Q: How frequently should maintenance be performed on a hydraulic rotating union?
A: Maintenance frequency can vary, but it often depends on the application’s demands. As a general rule, unions should be inspected at regular intervals, which might range from every few months to once a year. The manufacturer’s guidelines will provide a maintenance schedule appropriate for the specific model of the rotating union.
See What We Can Do

