In the intricate world of fiber optics, Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Rotary Joints (FORJs) play an exceptionally critical role. Acting as rotating interfaces, they allow the transmission of optical signals from a stationary to a rotating structure, a function vital for many technical applications.
Introduction to Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Rotary Joints
A rotary joint essentially provides a connection between two different parts, supporting relative rotation while transmitting data, signals, and power between them. When it comes to transmitting optical signals, we leverage devices known as Fiber Optic Rotary Joints.
The term “multi-mode” in Multi-Mode FORJs refers to the type of fiber being employed in the joint. Optical fiber, the conduit for these signals, comes in two primary varieties: single-mode and multi-mode. The “mode” here refers to the path that light waves take when traveling down the fiber.
Unlike single-mode fibers that guide light along a single path, multi-mode fibers have a larger core diameter, allowing them to transmit multiple light beams or modes simultaneously. With these multiple pathways for light, multi-mode FORJs can transmit a higher volume of data over a given period, though this comes with a shorter range compared to single-mode implementations due to modal dispersion.
In essence, Multi-Mode FORJs are crucial enablers of robust fiber optic technology. Their application extends from the telecommunications industry to advanced medical procedures, from military defense systems to entertainment and broadcast services. Their worth is indisputable, and understanding their role, operations, and benefits opens up a world of possibilities in the expansive field of fiber optics.
As we journey through this guide, we will delve further into the mechanics, advantages, applications, and important considerations for these innovative devices. Let’s embark on this exploration of multi-mode fiber optic rotary joints, deepening our understanding of how they contribute to the world of technology and communication.

Mechanics of Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Rotary Joints
To fully appreciate the role and benefits of Multi-mode FORJs, it’s essential to understand how they function within fiber optic systems. They are a marvel of technology and their operation principle is based on intricate optical and mechanical design.
As established in our introduction, the term “multi-mode” refers to the type of optical fiber used. These fibers possess a larger core – typically with diameters of 50 or 62.5 micrometers, significantly larger than the 9 micrometers typical of single-mode fibers. This larger core diameter allows multi-mode fibers to carry multiple light rays, referred to as modes, at the same time.
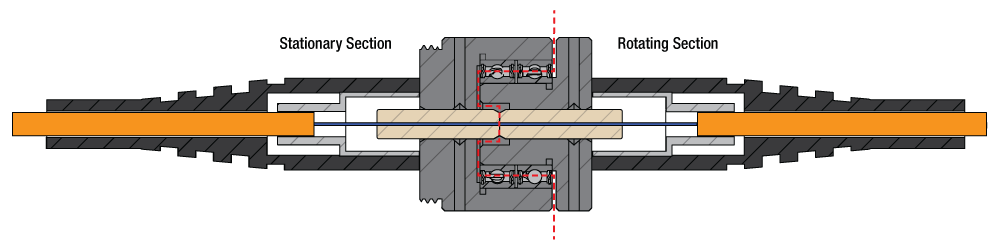
The basic working principle of all Fiber Optic Rotary Joints, including their multi-mode variant, involves ensuring that light is efficiently transmitted from a stationary fiber end to a rotating one, or vice versa. This transfer happens with minimal signal losses, reflections, or disruptions, and across many potential rotations without limitation.
In a Multi-Mode FORJ, the input light signal enters the rotating joint through the stationary multi-mode optical fiber. The input signal comprises multiple light modes, each carrying a portion of the data to be transmitted. It is then collimated by a lens into a light beam that travels towards a mirrored surface.
In the simplest form of a FORJ, the mirrored surface is a circular length of optical fiber that has been polished on one side to act as a mirror and mounted on the rotating component of the FORJ. This mirror rotates in accordance with the movement of the device to which the FORJ is fitted, ensuring that any collimated light beam aimed at it will be reflected back irrespective of the rotation angle.
The reflected light beam is then refocused into the rotating multi-mode fiber. Since the rotating fiber is also a multi-mode fiber, it can handle the multiple modes contained in the signal without significant loss or distortion. Though some modal dispersion may occur, this is typically not substantial over short-distance applications to affect signal integrity.
Over time, this unique functionality has been improved and additional complexities introduced to accommodate varying application conditions. Today’s multi-mode FORJs often incorporate advanced features such as multiple channels, wavelength division multiplexing, and integrated electrical slip rings to offer comprehensive solutions for even the most demanding applications.
In a nutshell, the mechanics of Multi-mode FORJs hinge on an efficient optical design that ensures high-fidelity light signal transmission across rotating interfaces. Understanding this allows us to see how valuable these devices are in a wide range of industries and applications. Our further sections will bring more light to these aspects.
Advantages of Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Rotary Joints
Multi-mode FORJs bring a multitude of benefits to the table compared to their single-mode counterparts or other types of rotary joints. Their unique design and inherent strengths are utilized in numerous applications across diverse industries. Let us explore these advantages and how they contribute towards making Multi-Mode FORJs befitting components in many vital scenarios.
- High Bandwidth Capacity: As we discussed earlier, multi-mode fibers have a larger core diameter, enabling the transmission of multiple light modes simultaneously. This results in Multi-Mode FORJs facilitating a larger volume of data to be transmitted at any given time, resulting in higher bandwidth capacity. This attribute gives them an edge in applications that require fast and high-volume data transfer.
- Short-Distance Efficiency: Multi-Mode FORJs excel in communication systems that cover short distances, typically up to a couple of kilometers. While single-mode fiber optic rotary joints might dominate in long-distance signal transmission, multi-mode joints hold the advantage for relatively shorter distances due to their lower attenuation, which minimizes signal loss.
- Cost-Effectiveness: In general, Multi-Mode FORJs tend to be more cost-effective compared to single-mode variants. This is primarily because multi-mode fibers are more economical to produce, and the transmitters that drive the light signals through these fibers come at a lower cost. For businesses searching for solutions that balance performance with cost, Multi-Mode FORJs can be an attractive choice.
- Robustness and Ease of Installation: Multi-mode fibers have a more extensive core compared to single-mode fibers, making them more tolerant of misalignments, and easier to connect. This results in more forgiving installation and maintenance experiences. Additionally, as they are less sensitive to back-reflections and splicing errors, the overall robustness and reliability of Multi-Mode FORJs are enhanced.
- Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure: Many existing fiber optic systems already employ multi-mode fibers, making Multi-Mode FORJs seamlessly compatible with this infrastructure. This advantage is particularly beneficial when upgrading, expanding, or maintaining such systems without completely replacing or overhauling their components.
- Flexibility in System Design: Given the above-highlighted benefits, Multi-Mode FORJs offer greater flexibility in system design. They can be successfully employed in diverse applications, providing fiber optic solutions steering towards high performance and cost-effectiveness.
In conclusion, Multi-Mode FORJs showcase impressive capabilities in various fiber optic communication systems and applications, thanks to their unique benefits. Industrial sectors seeking a powerful combination of high bandwidth capacity, short-distance efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced flexibility must consider these innovative devices at the forefront of their fiber optic deployments.

Comparison: Multi-mode vs. single-mode Fiber Optic Rotary Joints
A comprehensive comparison between Multi-Mode and Single-Mode Fiber Optic Rotary Joints provides valuable insights into where each type excels. It helps us understand why one can be a superior choice over the other for certain applications based on their distinctive properties and strengths. To add clarity to this discussion, let’s analyze these two types of FORJs along several key parameters.
Bandwidth and Data Transmission
Multi-mode FORJs have a distinct advantage when it comes to the simultaneous transmission of multiple data streams. The larger core diameter allows the utilization of multiple light modes, supporting a higher volume of data to be transmitted at once, thus providing higher bandwidth.
On the contrary, Single-Mode FORJs facilitate the transit of one light mode at a time, which limits their immediate bandwidth. Although they can yield higher bandwidths when paired with advanced modulation techniques, this can lead to additional system complexities and costs.
Transmission Distance
The strength of Single-Mode FORJs lies in their ability to transmit over longer distances without significant loss of signal integrity. This is due to the single path taken by light waves, which results in diminished modal dispersion, thereby preserving the quality of the transmitted signal over greater distances.
Multi-mode FORJs, however, are more optimal over shorter distances (typically up to a couple of kilometers). Their design results in modal dispersion, affecting signal quality over longer distances. Nevertheless, for shorter-distance applications, multi-mode joints perform exceptionally due to their lower attenuation and higher bandwidth availability.
Cost
When observing from a cost perspective, Multi-Mode FORJs generally offer a more cost-effective solution. The multi-mode fibers are less expensive to manufacture, and the transmitters and components required for these systems are typically less expensive than those required for single-mode systems.
Single-mode FORJs, however, might entail greater initial expenses due to the high-precision manufacturing process and the need for more expensive lasers for signal transmission. Over long-term use and vast distances, these costs might balance out due to their ability to maintain signal integrity over extreme lengths.
Installation and Maintenance
Multi-mode FORJs are often more tolerant of minor misalignments and other installation difficulties due to their larger core size. This leads to a more hassle-free installation and maintenance experience. They are also less sensitive to back-reflections and splicing errors, enhancing their overall robustness.
On the other hand, the installation and maintenance of Single-Mode FORJs may require more precision due to the smaller core size and its sensitivity to back-reflections and splicing errors.
In summary, both Multi-Mode and Single-Mode FORJs have their unique benefits and are better suited to different environments and applications. While the choice between the two largely depends on the specific requirements of the use case, this comparison provides a holistic perspective on the vital roles they play in the realm of fiber optics. Their distinct characteristics determine their suitability – where multi-mode outperforms in high-bandwidth, short-distance applications at a cost-effective rate, single-mode performs impeccably over long distances, maintaining signal integrity.
Applications of Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Rotary Joints
Multi-mode FORJs have solidified their crucial role in diverse applications due to their high bandwidth capabilities, cost-effectiveness, and proficiency in short-distance data transmission. They are particularly essential in scenarios where unrestricted, continuous rotation is required while simultaneously transferring optical signals. Let us delve into the key applications where Multi-Mode FORJs significantly contribute.
Data Centers
Multi-mode FORJs are utilized extensively in data centers across the globe. Their high bandwidth provision supports the immense data that needs to be transmitted swiftly within these centers. Their ability to efficiently manage short-distance transmissions makes them an optimal choice in these environments.
Medical Equipment
In the medical realm, devices such as computerized tomography (CT) scanners and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machines incorporate Multi-Mode FORJs. Their purpose is to transmit data from the rotating part of the machinery (like the gantry in a CT scanner) to the stationary computers responsible for data analysis. The continuous, unhindered rotation enabled by these FORJs is pivotal in carrying out uninterrupted medical imaging.
Renewable Energy
In the renewable energy sector, Multi-Mode FORJs find their use in wind turbines. They facilitate real-time data transfer from the nacelle to the stationary base, despite the continuous rotation of the turbine blades. This data transmission is key to monitoring turbine performance, weather conditions, and safety measures.

Telecommunication Networks
Telecommunication infrastructures employ Multi-Mode FORJs due to their excellent short-range performance and bandwidth capabilities. Within these networks, data exchange occurs intensively and requires an efficient, high-bandwidth solution, making Multi-Mode FORJs an invaluable component.
Industrial Automation
In the realm of industrial automation, robotic systems, and manufacturing equipment often employ Multi-Mode FORJs. These devices provide continuous 360° rotation without signal loss, ensuring smooth operation and data transmission within automation setups.
Marine Technology
Sea-based platforms or marine vessels often need continuous rotation and high-performance data transfer capabilities. Multi-mode FORJs can proficiently bear these conditions, making them an excellent choice for such environments.

Surveillance Systems
In surveillance systems, Multi-Mode FORJs are used in revolving or pan-tilt cameras. They permit constant, unrestricted rotation of these cameras while ensuring high-quality image data transmission to the control center.

In conclusion, Multi-Mode FORJs, with their distinctive strengths, cater to a wide variety of industries and applications, contributing significantly towards their efficient operations. This versatility is a testament to their technological ingenuity and adaptability in meeting today’s high-bandwidth, high-speed data communication demands.
Industry-Specific Usage of Multi-Mode FORJs
The adoption of Multi-Mode FORJs is on the rise owing to their unique advantages in numerous industries and sectors that demand high bandwidth, short-distance communications, and continuous rotational capabilities. Let’s explore some industries that significantly benefit from using Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Rotary Joints.
Defense and Aerospace
In defense and aerospace applications, Multi-Mode FORJs boost communication systems both on the ground and in airborne vehicles. The efficient data transmission capabilities provided by these devices are essential for secure, real-time, high-definition video feed transmission between rotating systems, such as radar installations and tracking devices mounted on autonomous or remotely piloted vehicles.

Broadcasting Industry
In the broadcasting sector, Multi-Mode FORJs are used in live event coverage, where video cameras continuously rotate to follow ongoing performances or games. The FORJs ensure smooth transmission of high-quality video signals from the rotating cameras to the stationary control rooms, enabling flawless live stream and capture.
Geophysical Exploration
In the geophysical exploration industry, various sensors and rotary tools are used to study and map the Earth’s subsurface. Multi-mode FORJs, configured with these tools, facilitate the uninterrupted transmission of crucial data extracted by the rotating sensors. They facilitate real-time data transfer and analysis, which is vital for the industry’s overall success.
Oil and Gas
In the oil and gas sector, drilling equipment often encounters high rotation rates, harsh environments, and extensive data collection requirements. Multi-mode FORJs handle these arduous conditions and ensure timely data delivery to the surface, further assisting in monitoring drilling processes and making informed decisions.

Entertainment Industry
The Entertainment industry uses Multi-Mode FORJs in areas like theme parks, where media installations require unrestricted rotations while simultaneously transmitting high-resolution audio and video signals to control systems. Also, augmented or virtual reality simulators built for immersive experiences use such technology for seamless data transfer.

Research and Development
In research and development laboratories, Multi-Mode FORJs are employed to maintain high bandwidth capacity when devices, such as centrifuges or rotatory test chambers, require uninterrupted data transmission. Their usage enables precise measurement and accurate evaluations in different lab equipment and experiments.
The wide range of industry-specific applications exemplifies the impact of Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Rotary Joints across multiple domains. These indispensable devices bolster high-performance communication and data transfer, providing efficient, reliable solutions for many demanding and rigorous environments. It is undoubtedly clear that the future of fiber optics will continue to expand in tandem with innovative advancements within these industries.
Factors to Consider Before Investing in Multi-Mode FORJs
Before investing in Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Rotary Joints (FORJs), it’s crucial to understand the key considerations that will ensure their optimal operation, durability, and successful integration into an existing system. Here are some pivotal factors to keep in mind when purchasing these devices:
Application Needs
The foremost element to consider is your specific application requirement. You need to be clear about your data transmission needs (volume and speed), rotation functionality, and required distance for data transfer. Multi-Mode FORJs work best for high-bandwidth, short-distance (up to a few kilometers), and simultaneous multiple data streams transmission.
Environmental Factors
The operating environment can significantly impact FORJs’ performance. Whether it’s a dry, climatically controlled environment such as a data center, a harsh outdoor location like a wind farm, or a sensitive medical setup, an understanding of the environment plays a critical role in choosing the right FORJ.
Power Budget
Understanding your power budget is crucial. Depending on the nature of your data transmission, a certain amount of power loss may be acceptable. However, if the power budget is tight, it might be necessary to consider the signal loss over the transmission distance and the total loss at connectors and splices.
Quality and Performance
Invest in a FORJ with a consistent performance record and high quality. Look for devices with low insertion loss, low return loss, low cross-talk, and high rotational life.
Durability and Maintenance
A durable FORJ reduces maintenance needs and downtime. Consider the construction material, maintenance requirements, and the ability of the device to withstand the rigors of your application.
Compatibility
Ensure the FORJ is compatible with your existing fiber optic systems. Compatibility with your specific fiber type and the connector style used in your system is crucial for an efficient setup.
Provider’s Expertise
The manufacturer’s expertise and reputation in the industry also play a key role. Trust companies that have a proven record of providing top-quality devices and excellent ongoing support.
Future Expansion
Consider your future expansion plan. It’s a good idea to invest in a device that can scale up according to future needs.
In conclusion, a handful of factors can determine the success of an installation of a Multi-Mode ForJ in different setups. Thorough market research complemented by the understanding of your specific application needs is the first step towards making an informed decision. Remember, the right choices lead to increased efficiency and longevity of the communication system.
Conclusion
In sum, multi-mode FORJs clearly play a vital role in modern data transmission systems. With their unique advantages and wide application in various industries, understanding them can help professionals make informed choices and utilize them optimally in their operations.
Need more information on Fiber Optic (FORJ) RF Rotary Joints? Complete the form below, and our experts will assist you.
FAQs about Multi-Mode FORJs
Below are some of the commonly asked questions related to Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Rotary Joints (FORJs), aiming to address potential uncertainties or misconceptions and provide a comprehensive understanding of these critical devices.
Q: What is a Multi-Mode FORJ?
A: A Multi-Mode FORJ is a device that provides the ability to pass optical signals across a rotating interface while preserving the properties of the optical signal. Multi-Mode FORJs are used primarily within short distances due to their high capacity to transmit larger volumes of data at higher speeds.
Q: How does a Multi-Mode FORJ work?
A: At a basic level, a Multi-Mode FORJ works by coupling light from an input fiber to an output fiber, even as these two fibers rotate relative to each other. The device employs optics to maintain the alignment and focus of the signal, ensuring the data is transferred effectively and efficiently.
Q: Why is a Multi-Mode FORJ needed?
A: Multi-mode FORJs are essential in any application where unrestricted, continuous rotation is required while also allowing for the transfer of optical signals. They play a crucial role in industries such as telecommunications, data centers, renewable energy, defense, and more.
Q: When would one use a Single Mode FORJ instead of a Multi-Mode FORJ?
A: Single-mode FORJs are chosen over multi-mode FORJs when data need to be transmitted over longer distances (up to 100 km). They are also used when the system demands lower signal loss and higher bandwidth, albeit requiring a higher precision of alignment.
Q: Are Multi-Mode FORJs compatible with all fiber optic systems?
A: Not necessarily. A Multi-Mode FORJ needs to be compatible with the specific type of fiber optic cable being used in a particular system. And it has to be matched to the specific connector styles used in that system. Therefore, it’s important to check the compatibility of the FORJ with your system before purchasing.
Q: How do I maintain a Multi-Mode FORJ?
A: Maintenance of a Multi-Mode FORJ typically depends on the specific model and its use case. However, regular cleaning of optical surfaces and periodic performance checks are general practices for maintaining optimal performance.