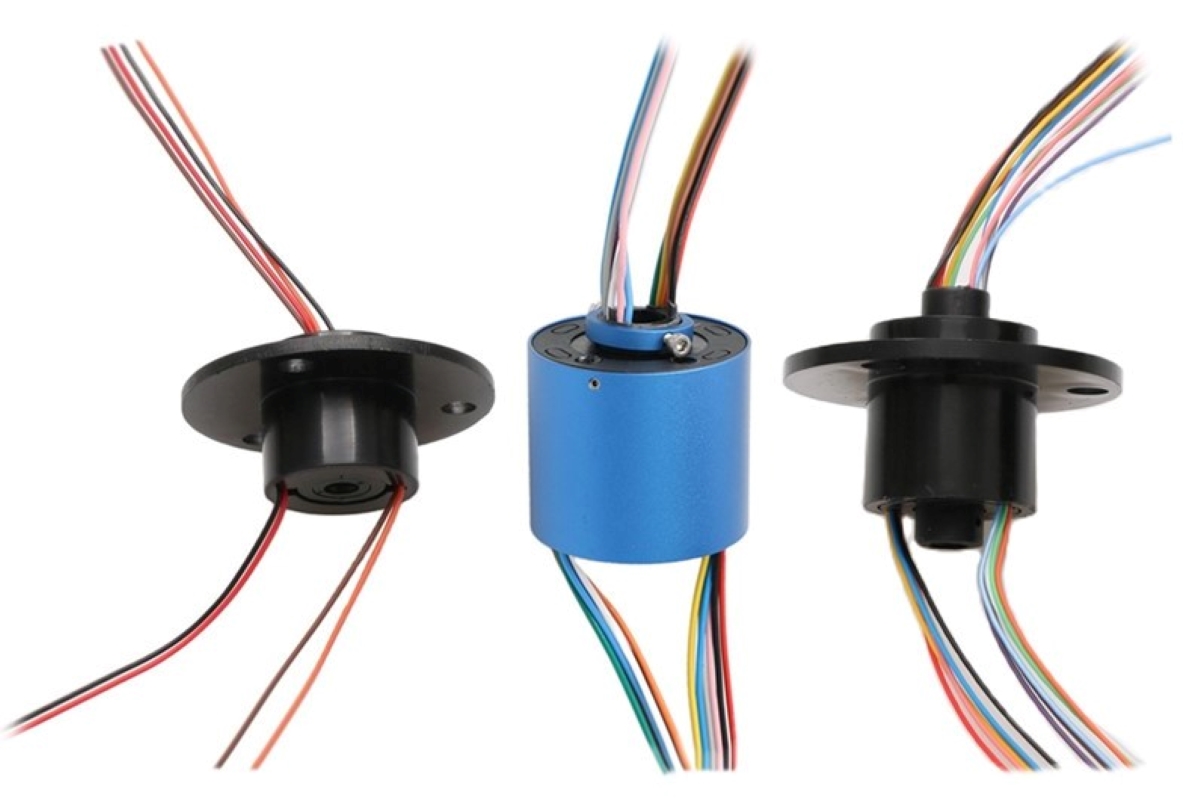
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the intricacies of connector electrical—the unsung heroes that empower and facilitate modern technology. From its fundamental history to the innovative future trends transforming the landscape, we examine all facets of electrical connectors. We begin with an insightful introduction to the concept of connectors, sketching their evolution and underlying importance in our daily lives. The article then navigates through the diverse types of connectors, such as terminal blocks, plugs, sockets, and busbars, highlighting their specific applications, unique features, and advantages. Understanding the criticality of choosing the right connector, we provide expert guidance on selection criteria including current, voltage, environmental conditions, and connector design. Practical insights on installation, safe usage, and meticulous maintenance offer readers a foundational grasp on handling these connectors effectively. Moreover, safety measures underscore the vital precautions necessary when working with electrical connectors. The piece culminates by casting a look toward the future, discussing innovations and forecasting trends that could redefine electrical connectivity. Join us in this engaging journey that not only underscores the vital role of connectors in technology but also prepares you for the advancements lying on the horizon.
Introduction to Connector Electrical
The Inception of Electrical Connectors: Tracing Back the Origins
The story of electrical connectors begins in the early days of electrical engineering when inventors were trying to find efficient ways to join wires and components together. Before the standardized electrical connectors, we know today, early electrical systems relied on makeshift, often unreliable connections that could lead to inconsistent performance and even safety hazards. The evolution of connectors paralleled technological advancements, with each innovation in electricity and electronics necessitating more refined and reliable connections. From simple screw terminals to sophisticated multi-pin connectors, the journey of electrical connectors is a testament to the relentless pursuit of efficiency, reliability, and safety in electrical engineering.
Pivotal Roles in Daily Operations: Why Connectors Matter
In our modern world, electrical connectors are unsung heroes. Virtually every electronic device, from the simplest toys to the most complex supercomputers, relies on them. They are the critical junctions that allow electrical current to flow seamlessly across circuits, ensuring that our gadgets, appliances, and industrial Machinery operate as intended.

Consider, for example, the role of connectors in healthcare. Medical devices, from patient monitors to advanced imaging equipment like MRI machines, depend on highly reliable connectors to function correctly. In such applications, the right connector not only ensures device effectiveness but is also pivotal to patient safety.
In the realm of consumer electronics, connectors impact not just functionality but also user experience. The USB connectors that charge our phones and transfer data between devices are a prime example. The evolution from USB-A to USB-C has not only enhanced data transfer rates and charging speeds but also significantly improved the user experience with its reversible design.
Similarly, in the automotive industry, as vehicles become more electric and digitally connected, the importance of electrical connectors has surged. Whether it’s for connecting advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), in-car entertainment systems, or the intricate network of sensors in electric vehicles (EVs), each connector must ensure reliability in harsh conditions, including vibrations, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to liquids.
Through these examples, the significance of electrical connectors in our day-to-day lives becomes evident. They are fundamental components that don’t just connect circuits; they connect us to our technology and facilitate the smooth functioning of the devices and systems that power our modern lives.
Addressing Common Curiosities and Concerns
A common question surrounds the durability and longevity of connectors, particularly in environments subject to extreme conditions. How do connectors maintain their reliability over time, and what innovations are manufacturers implementing to enhance their performance? Understanding the materials used, the design considerations for different environments, and the testing procedures can shed light on these aspects.
Moreover, the environmental impact of connectors is another area of interest. As the world moves towards sustainability, the electronics industry is innovating to produce connectors that are not only efficient and reliable but also made from eco-friendly materials and designed for easy recycling.
In wrapping up this introduction, electrical connectors might seem like simple components, but their role in the seamless functioning of electrical and electronic systems cannot be overstated. From enabling our daily conveniences to powering critical infrastructure, their invisible work underpins the technological advances of our era. By delving into the history, importance, and future of connectors, we gain a deeper appreciation for these crucial components and the intricate roles they play in our electrified world.
Different Types of Connector Electrical: A Deep Dive into Varieties and their Applications
Explore the universe of electrical connectors, and you will find an astonishing variety of types, each designed to meet specific applications, with unique features and corresponding advantages. This chapter presents a closer look at these diverse players, from terminal blocks to plugs and sockets, busbars, and more.
Terminal Blocks: The Fundamental Connector
Terminal blocks, also known as terminal barriers or connection terminals, are a straightforward type of connector used to connect two or more wires together securely. Available in several types dependent upon the application, these include PCB terminal blocks, power distribution blocks, and pluggable terminal blocks, among others. For example, in home automation systems, terminal blocks might be used to connect wires for lighting, security, or smart appliance controls. Their modularity and flexibility of use are hallmarks of their design.
Plugs and Sockets: Powering Everyday Connections
Almost every electronic device we use in our daily lives, including computers, televisions, kitchen appliances, and even smartphone chargers, relies on plugs and sockets for power supply and connectivity. Their purpose is established the world over – to plug into a power source safely, easily, and reliably. However, designs and specifications often vary by geographical location, respecting the individual safety standards and voltage requirements of each region.
Busbars: The Backbone of Power Distribution
Busbars serve as the main conductor in an electrical panel, distributing power across the board. These heavily insulated conductive bars can handle large current loads, making them indispensable in industrial applications. From power plants to large commercial buildings, busbars ensure smooth, heavy-duty power distribution with high efficiency and safety.
Connectors in Focus: Use Cases and Advantages
The specific application of each connector type defines their design. An interesting case study is the use of connectors in electric vehicles (EVs). In EVs, connectors must be able to handle high power levels and ensure safety and reliability even under harsh conditions. Therefore, these applications often require specialist connector types capable of maintaining efficient electrical connections over long periods, in variable weather conditions, and under constant vibration—everything that a road vehicle is subjected to.
High-speed digital connectors are another example. As our need for data transmission continues to increase exponentially, so does the requirement for connectors that can support high-speed communication. Today’s cutting-edge digital connectors make possible the rapid communication of data between devices, functioning as the essential veins of our information-heavy environments.
In conclusion, the world of connector electrical is diverse and dynamic, populated by a wide array of types each boasting unique features and advantages. Knowledge and understanding of this landscape is key to selecting the right connector for the right purpose and ensuring safety, reliability, and high performance in every application.
How to Choose the Right Connector Electrical: Navigating the Choices
Choosing the right electrical connector is a blend of science and art – it requires a nuanced understanding of the electrical needs of the system, consideration of ambient environmental parameters, and application-specific design constraints. This chapter presents a step-by-step guide to navigating this technical landscape and equips you to make the correct choices.
Understanding Your Electrical Specifications: Current and Voltage
The critical starting point in selecting a connector is understanding the electrical specifications of the device or system it will be used for. The current requirement (I) and voltage (V) are paramount to consider as they directly impact the kind of connector you should choose.
- Current: The connector must be capable of handling the highest current it could possibly see in the application. Consider an EV charging station delivering a high current feed to the vehicle. An under-specified connector will heat up, potentially damaging itself and the charging unit, or even leading to a fire.
- Voltage: The connector should withstand the highest voltage levels in the application. Ensuring the connector’s dielectric strength (the maximum voltage it can resist without breaking down) matches or exceeds the system’s voltage requirement is vital for safety and reliability.
Think of electrical connectors as water pipes: higher current is like a higher quantity of water, and higher voltage is like higher water pressure. Just as you would need bigger, stronger pipes for more water or higher pressure, you need heavier-duty connectors for higher current and voltage.
Considering the Operating Environment
By its very nature, electricity is affected by the surrounding environment. High temperatures can raise resistance and lower electrical conductivity.
- Temperature: If your connector is expected to withstand high temperatures, it needs to be designed from materials that can tolerate such conditions without failing or losing efficacy.
- Humidity and Exposure to Water/Air: If the connector is to be used in a damp environment or could be exposed to liquid (like in a dishwasher or marine application), it should have a high Ingress Protection (IP) rating, which illustrates its ability to resist water ingress.
- Mechanical Strains and Vibrations: Another frequent challenge is in automotive or aerospace applications, where connectors endure regular vibrations and mechanical strains. Here, toughness and reliability become crucial qualities in choosing connectors.

Connector Design and Physical Constraints
Matching the connector to the physical space and mounting options is another critical piece of the selection puzzle.
- Space: Miniaturization in electronics means connectors too need to be smaller, yet carry higher data or power loads. Knowing the available space helps you to choose an appropriately sized connector for the application.
- Mounting Style: There are different mounting styles like panel mount, free-hanging, or PCB mount, etc. Your choice depends on your specific application. An automotive sensor may require a panel-mounted connector, while a computer circuit board will use a PCB-mounted one.
- Number of Contacts: Finally, the number of signals, power, or data lines that need to be connected will determine how many contact points you require in your connector.
Real-World Example: Connector Selection for a Wind Turbine
Consider the example of a wind turbine. The tower’s height exposes connectors in the nacelle (the housing for the generator) to temperature extremes, winter icing, and summer heat. Furthermore, the rotation of the blades subjects them to continuous, pronounced mechanical stress.
Here, an appropriate connector would be one with a high IP rating (for weather resistance), excellent tolerance for mechanical stress (to withstand vibration), and a design robust enough to handle the system’s high voltage and current.
An important final pointer is to revisit your choice after prototype testing and initial deployment. It’s vital to check whether the connector meets your expectations in the real world and iterate as needed, which ensures the reliability and longevity of your electrical systems.
This guide aims to empower you, unraveling the complexities of connector selection. With these insights, you’re now better equipped to navigate through the maze of choices and pick the right electrical connector. In the words of the maxim, “Choose wisely.” Your electrical system’s reliability, efficiency, and longevity could well depend on it.
Installation and Use of Connector Electrical: A Comprehensive Guide
The proper installation and use of electrical connectors are critical to the safety and functionality of any electrical system. This guide walks you through each step with clarity and precision, ensuring that you apply best practices to prevent malfunctions and ensure safe operation.
Step-by-Step Connector Installation
The installation process can vary widely between different types of connectors, but here we’ll discuss a set of general principles that can be applied across the board, accompanied by clearer pointers for common connector types.
Preparation: Begin by gathering all necessary tools. This will vary depending on the connector type but may include wire strippers, crimping tools, soldering iron, or screwdrivers.
Ensure the power source is switched off to prevent electrocution.
Stripping and Cutting: Measure and cut your wires to the correct length for your application, granting enough slack for maintenance.
Strip the insulation from the end of each wire using wire strippers. Be cautious not to strip too much or little or damage the conductor.
Securing the Wires: For screw terminals, unscrew the terminal screws enough to insert the wire. For crimp connectors, place the wire into the crimp barrel.
Ensure that there are no stray strands that could cause a short. If soldering, tin the wire ends and the connector contacts to ensure a strong joint.
Testing: Once connected, make sure the wires are securely fixed to the connectors.
Test the connection with a multimeter to ensure there is continuity and no short circuits.
Tips for Safe and Effective Use
Just as installation requires diligence, effective use of electrical connectors requires ongoing attention.
- Regular Inspection:
Regularly inspect connectors for signs of wear and tear, such as corrosion or damage that could compromise safety or functionality. - Proper Handling:
Always grip connectors by the housing when making or breaking connections, never by the wires, to prevent stress on the connection points. - Environmental Consideration:
Be mindful of the connector’s environmental ratings (IP rating). Do not expose connectors to environments they are not rated for, such as wet or dusty conditions.
Case Study: Ensuring Reliability in Industrial Machinery
In an industrial setting, a faulty connector installation on a critical machine such as an induction motor can result in significant downtime and repair costs. Proper installation, therefore, is not only a safety measure but a business imperative. For instance, an induction motor used in a food processing plant might have washdown requirements for cleaning. In this case, selecting a connector with a high IP rating is necessary, but improper installation could negate its benefits, leading to water ingress and eventual motor failure.
Addressing Common Questions and Misconceptions
- “All connectors are the same, right?”
No, connectors come with different ratings for current, voltage, and environmental conditions, and must be selected and installed with these specifications in mind. - “I’ve installed the connector – am I done?”
Post-installation includes regular checks, especially after any incident that could compromise the integrity of the connectors, such as an electrical surge or physical impact.
Closing Recommendations
A well-chosen and properly installed connector not only serves as the bridge between components in an electrical system but also enhances the system’s reliability and safety. While the protocol outlined here serves as a solid foundation, always consult the specific installation guidelines provided by the connector manufacturer for best results.
The safe and effective use of electrical connectors is an instrumental aspect of electrical system design and maintenance. This guide aims to instill a comprehensive understanding of both the technical and practical aspects, underlining the importance of getting it right for the sake of both functionality and safety. By combining this knowledge with regular maintenance and inspections, you will ensure that your connectors—and therefore your electrical systems—operate reliably and safely for years to come.
Safety Measures When Handling Connector Electrical : Protecting Yourself and Your Equipment
Working with electrical connectors involves more than just ensuring a firm and proper connection between two components. It’s about safeguarding one’s personal safety and the operational integrity of the electrical system. Ignoring safety measures can lead to dire consequences, including electrical fires, equipment failure, and personal injury. This section outlines critical safety protocols for handling electrical connectors with an emphasis on practical, real-world applications.
Understanding the Risks
Before delving into safety measures, it’s important to comprehend the potential risks involved in working with electrical connectors. Mismanagement can lead to short circuits, electric shocks, and even fires. Recognizing these hazards is the first step toward mitigating them.
Power Shutdown
- Disconnecting Power Sources: Always disconnect devices or systems from their power source before attempting any work on electrical connectors. This might seem elementary, yet it’s frequently overlooked, often with hazardous outcomes.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Essential PPE: Depending on the environment and the voltage levels being handled, wearing insulated gloves, protective eyewear, and flame-resistant clothing can be crucial. It’s not just about direct electrical hazards—flying sparks or debris can cause injuries.
Tools and Equipment
- Using Insulated Tools: When working on or near live circuits (which should be avoided as far as possible), use tools with insulated handles to reduce the risk of electrical shock.
Awareness and Environment
- Work Area Safety: Ensure the work area is dry and free from water to reduce the risk of electric shock. Standing on a rubber mat and ensuring there are no flammable materials nearby are good safety practices.
Best Practices for Connector Handling
- Correct Connector Use: Always ensure that the electrical connector you are using is rated for the voltage and current of the application. Incorrectly matching connectors to the application can lead to overheating and failure.
Case Study: Preventing Workplace Accidents
A manufacturing facility experienced frequent equipment failures and faced several near-miss incidents with electric shocks. An audit revealed two critical oversights: workers were often handling live connections, and the use of appropriate PPE was inconsistent. The introduction of strict lockout/tagout procedures and mandatory PPE use dramatically reduced incidents, underscoring the importance of safety protocols when working with electrical connectors.
Addressing Questions and Misconceptions
- “It’s just a low-voltage connector, why all the fuss?”
Even low-voltage connectors can pose a risk, particularly in terms of short-circuit creating a fire hazard. Safety is paramount regardless of voltage. - “I’ve done this a thousand times without gloves; why start now?”
Accidents can happen to anyone, and previous good fortune doesn’t guarantee future safety. Protective gear is a simple measure to mitigate risk.
Key Takeaways
The handling of electrical connectors, crucial as it is, comes with inherent risks that require diligent safety measures. It starts with the basic step of powering down equipment and extends through the use of protective gear, the right tools, and a safe work environment.
The proper handling and installation of electrical connectors are not only about ensuring system efficiency but also about preventing accidents that can have dire consequences. By adhering to these safety standards, individuals not only protect themselves but also ensure the longevity and reliability of the electrical systems they work on.
Remember, safety in the workplace is not an accident. It’s a deliberate and continuous effort to recognize, evaluate, and mitigate risks. Equip yourself with knowledge, use protective gear, and never underestimate the importance of safety precautions when working with electrical connectors, no matter how routine the task may seem.
Connector Electrical Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Ensuring Reliability over Time
Electrical connectors play a pivotal role in the robustness and reliability of electrical systems. However, over time, these critical components can become the very source of system failures if not properly maintained or when issues are left unaddressed. Understanding how to keep connectors in top condition and how to troubleshoot common problems efficiently can save both time and resources, while also preventing potential system downtimes. This section offers insights into maintaining connectors and steps for troubleshooting, enriched with real-world application insights.
Recognizing Symptoms of Connector Problems
The first step towards effective maintenance and troubleshooting is recognizing the early signs of connector issues. Symptoms can range from intermittent power loss, unusual heating at connection points, visible corrosion, and in some cases, odor or smoke indicating burning. These signs should not be ignored, as they can escalate into more significant problems.
Maintenance Best Practices
Regular maintenance can preempt a lot of potential connector problems. Here are some proactive measures:
- Visual Inspections: Periodically examine connectors for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. This simple step can identify many issues before they become critical.
- Cleaning Connections: Keeping connectors free from dust, dirt, and debris is essential for maintaining optimal performance. Use appropriate cleaning agents to avoid damaging the connectors.
- Ensuring Tight Connections: Loose connections can lead to arcing and overheating. Make it a routine to check and tighten connections where applicable.
- Environmental Protection: For connectors exposed to harsh environments, consider using protective covers or applying anti-corrosion treatments to prevent deterioration.
Troubleshooting Steps
When facing electrical issues that you suspect stem from connector problems, the following troubleshooting steps can be helpful:
- Power Down: Always ensure the system is powered off before attempting any troubleshooting to avoid the risk of electric shock.
- Visual Inspection: Check for obvious signs of damage or wear. This includes inspecting both the connector and the cable.
- Check for Loose Connections: A common issue is simply that connections have become loose over time. Tightening them may resolve the issue.
- Continuity Testing: Using a multimeter, check for continuity in the connection. Lack of continuity could indicate a broken wire or faulty connector.
- Cleaning Contacts: Sometimes, the issue can be as straightforward as dirty or oxidized contacts, preventing good electrical connection. Cleaning the contacts may restore functionality.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many connector issues can be resolved with the troubleshooting steps above, certain situations warrant professional attention. If you encounter severe damage, signs of burning, or complex system issues that aren’t resolved through basic troubleshooting, it’s time to call in a professional. This is especially important in systems where safety could be compromised, such as high-voltage applications or where the integrity of a critical system is at stake.
Real-World Case Study: Industrial Plant Overcomes Downtime
An industrial plant faced repeated downtime due to equipment failures traced back to connector issues in a critical control system. Routine maintenance had been neglected, and corrosion had set in, exacerbated by the plant’s humid environment. Implementing a scheduled maintenance program, including regular inspections and the use of corrosion-resistant connectors, resolved the downtime issues, highlighting the critical role of connector maintenance in industrial settings.
Addressing Common Questions and Concerns
- “Can’t I just replace the connector if there’s an issue?”
While replacement is sometimes necessary, understanding the underlying problem is crucial to prevent recurrence. Plus, troubleshooting can often save time and resources. - “Why bother with maintenance? Connectors are cheap to replace.”
The cost of the connector itself might be low, but the potential costs due to system downtime, loss of productivity, or safety incidents far outweigh the maintenance effort.
Concluding Reflections on Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Efficient maintenance and effective troubleshooting of electrical connectors are non-negotiable aspects of managing any electrical system, from household appliances to industrial machinery. By adopting a proactive approach towards connector care and being equipped with basic troubleshooting skills, most common connector issues can be resolved swiftly, ensuring that the electrical systems remain operational, safe, and reliable over their lifespan. Remember, the goal is not just to fix problems as they arise but to prevent them from occurring in the first place.
Innovation and Future Trends in Connector Electrical : Shaping the Next Generation of Connectivity
The realm of electrical connectors, often perceived as a static domain of mere nuts and bolts of the electrical world, is undergoing a profound transformation. Innovations are not only refining the existing attributes like efficiency and durability but are also steering these components towards uncharted territories of functionalities and applications. This chapter delves into the latest trends in the industry, underlining the ingenious advancements in connector design and forecasting the technological leaps that may redefine the future landscape of electrical connectivity.
The Vanguard of Innovations
Miniaturization and High-Density Connectivity
In the quest for compactness without compromising performance, the trend of miniaturization stands prominent. Modern connectors are being designed to fit into increasingly smaller spaces, catering to the needs of sophisticated gadgets and industrial machinery alike. High-density connectors, which offer more connections in a confined space, are becoming ubiquitous in applications ranging from consumer electronics to aerospace, emphasizing efficiency and space-saving.
Enhanced Durability and Reliability
Materials science has played a pivotal role in elevating the durability and reliability of connectors. Innovations in corrosion-resistant alloys and advanced plastics are ensuring that connectors can endure harsh environments, from the corrosive salt waters of the ocean to the vacuum of space. Furthermore, advancements in sealing technologies offer improved protection against moisture and dust, cementing the reliability of connections in adverse conditions.
Smart Connectors: Beyond Simple Connectivity
Enter the era of smart connectors, which are equipped with sensors and chips to monitor, record, and analyze the state of the electrical connection and the environment around them. These connectors can predict failures, ensuring preventive maintenance can be carried out, thereby reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of the equipment. By integrating communication capabilities, smart connectors are paving the way for interconnected and intelligent systems, a cornerstone of the IoT (Internet of Things) revolution.
Envisioning the Future
Wireless Power Transfer and Connectivity
The prospect of wireless power, coupled with data transfer through connectors, is inching closer to reality. This technology aims to eliminate physical connections, reducing wear and tear, and enabling more flexible and efficient system designs. Imagine charging electric vehicles or powering household appliances without needing to plug them in, a future that seems ever more plausible.
Nanotechnology and Quantum Computing Implications
Nanotechnology promises to dramatically scale down connectors while enhancing their performance, a critical development for the burgeoning field of quantum computing. Quantum computers, with their extraordinary computing power, will necessitate connectors capable of operating at extremely low temperatures and handling high-speed quantum data transfers, pushing the envelope of connector technology.
Environmental Sustainability and Bio-Friendly Materials
The increasing emphasis on environmental sustainability is driving the adoption of bio-friendly materials and recyclable components in connector design. Future connectors could be fashioned from biodegradable materials or designed for easy disassembly, ensuring minimal environmental impact and supporting circular economy initiatives.

Real-World Case Study: Revolutionizing Medical Devices
A notable example of innovation in connector technology can be seen in the medical device industry. A manufacturer developed a series of miniature, high-density connectors that are now used in wearable health monitors. These devices track patient data in real time, contributing to early diagnosis and personalized medicine. The connectors’ small size and reliability are crucial for the functionality and comfort of wearable devices, showcasing the potential of advanced connector technologies to enhance healthcare.
Addressing Common Questions and Concerns
- “Are smart connectors vulnerable to security threats?”
While introducing intelligence into connectors opens up new functionalities, it also raises legitimate cybersecurity concerns. Ongoing research focuses on embedding robust encryption and security measures directly into these smart components to safeguard data integrity and privacy. - “How quickly will these innovations become mainstream?”
The pace of adoption varies by industry and application. Consumer electronics tend to adopt innovations rapidly due to competitive pressures, whereas sectors like aerospace and healthcare may move more cautiously due to stringent regulatory standards.
Concluding Insights on the Future of Electrical Connectors
The landscape of electrical connectors is evolving at an unprecedented pace, fueled by relentless innovation and the drive towards smarter, more efficient, and sustainable systems. As we stand on the cusp of these transformative trends, it becomes evident that connectors—though small and seemingly inconsequential—are integral to powering the future of technology. By staying attuned to these advancements and fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation, industries can leverage the full potential of the next generation of electrical connectors, shaping a future where connectivity knows no bounds.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Electrical Connectivity
As we approach the culmination of our exploration into the world of electrical connectors, it’s imperative to reflect on the critical takeaways and the expansive potential that lies within these modest components. This journey revealed not only the foundational importance of connectors in ensuring the efficiency and reliability of electrical systems but also highlighted the vibrant innovations and future possibilities poised to redefine their role further.
Key Takeaways
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Regular maintenance, including visual inspections, cleaning, and ensuring tight connections, is paramount to prolonging the life and reliability of connectors. Effective troubleshooting techniques, such as continuity testing and examining for loose connections, are essential skills for mitigating issues and ensuring the optimal performance of electrical systems.
- Innovations Transforming the Field: The advent of miniaturization, high-density connectivity, enhanced durability, and the emergence of smart connectors illustrates the dynamic evolution of connector technology. These advancements are not merely incremental improvements but are pivotal in enabling the next generation of electrical systems and devices, from wearable technology to advanced aerospace applications.
- The Horizon of Future Connectivity: The anticipation of developments like wireless power transfer, nanotechnology, and the incorporation of bio-friendly materials underscores the forward momentum of the connector industry. Such innovations promise to address the growing demands for efficiency, sustainability, and seamless integration in various sectors.
- Real-World Applications and Impacts: Through lenses such as the medical device industry case study, we’ve observed firsthand the transformative impact of advanced connectors. These real-world examples serve as a testament to the potential of innovative connector technologies to drive progress, improve lives, and power the future.
The Path Forward
As we stand at the threshold of new technological eras marked by IoT, quantum computing, and an ever-increasing focus on sustainability, the role of electrical connectors becomes more integral and complex. The journey ahead for connectors, from fundamental components to intelligent, high-performance interfaces, reflects the broader trajectory of technological innovation and its pervasive impact on our world.
Invitation for Engagement
This exploration into the realm of electrical connectors, while comprehensive, only scratches the surface of the possibilities and challenges that lie ahead. Your experiences, insights, and questions are invaluable as we navigate this dynamic landscape together. Whether you’re troubleshooting a pesky connector issue, innovating the next generation of smart connectivity, or exploring sustainable materials for future designs, your journey contributes to the collective advancement of electrical connectivity.
We invite you to share your experiences, thoughts, or inquiries regarding the fascinating world of electrical connectors. Have you encountered an innovative application of connectors that reshaped your approach to design or maintenance? Are there areas of concern or curiosity that you wish to explore further? Engaging in these conversations not only enriches our collective understanding but also sparks innovation and collaboration within the community.
Embracing the Future Together
In closing, the discourse surrounding electrical connectors encompasses far more than mere technicalities—it’s about envisioning and shaping the future of technology, connectivity, and sustainability. By staying informed, proactive, and open to dialogue, we can collectively harness the profound potential of electrical connectors to power advancements across industries and impact lives positively. The future of electrical connectivity is not written in stone; it is shaped by our innovations, decisions, and shared aspirations.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Connector Electrical
As we approach the culmination of our exploration into the world of electrical connectors, it’s imperative to reflect on the critical takeaways and the expansive potential that lies within these modest components. This journey revealed not only the foundational importance of connectors in ensuring the efficiency and reliability of electrical systems but also highlighted the vibrant innovations and future possibilities poised to redefine their role further.
Key Takeaways
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Regular maintenance, including visual inspections, cleaning, and ensuring tight connections, is paramount to prolonging the life and reliability of connectors. Effective troubleshooting techniques, such as continuity testing and examining for loose connections, are essential skills for mitigating issues and ensuring the optimal performance of electrical systems.
- Innovations Transforming the Field: The advent of miniaturization, high-density connectivity, enhanced durability, and the emergence of smart connectors illustrate the dynamic evolution of connector technology. These advancements are not merely incremental improvements but are pivotal in enabling the next generation of electrical systems and devices, from wearable technology to advanced aerospace applications.
- The Horizon of Future Connectivity: The anticipation of developments like wireless power transfer, nanotechnology, and the incorporation of bio-friendly materials underscores the forward momentum of the connector industry. Such innovations promise to address the growing demands for efficiency, sustainability, and seamless integration in various sectors.
- Real-World Applications and Impacts: Through lenses such as the medical device industry case study, we’ve observed firsthand the transformative impact of advanced connectors. These real-world examples serve as a testament to the potential of innovative connector technologies to drive progress, improve lives, and power the future.
The Path Forward
As we stand at the threshold of new technological eras marked by IoT, quantum computing, and an ever-increasing focus on sustainability, the role of electrical connectors becomes more integral and complex. The journey ahead for connectors, from fundamental components to intelligent, high-performance interfaces, reflects the broader trajectory of technological innovation and its pervasive impact on our world.
This exploration into the realm of electrical connectors, while comprehensive, only scratches the surface of the possibilities and challenges that lie ahead. Your experiences, insights, and questions are invaluable as we navigate this dynamic landscape together. Whether you’re troubleshooting a pesky connector issue, innovating the next generation of smart connectivity, or exploring sustainable materials for future designs, your journey contributes to the collective advancement of electrical connectivity.
We invite you to share your experiences, thoughts, or inquiries regarding the fascinating world of electrical connectors. Have you encountered an innovative application of connectors that reshaped your approach to design or maintenance? Are there areas of concern or curiosity that you wish to explore further? Engaging in these conversations not only enriches our collective understanding but also sparks innovation and collaboration within the community.
Embracing the Future Together
In closing, the discourse surrounding electrical connectors encompasses far more than mere technicalities—it’s about envisioning and shaping the future of technology, connectivity, and sustainability. By staying informed, proactive, and open to dialogue, we can collectively harness the profound potential of electrical connectors to power advancements across industries and impact lives positively. The future of electrical connectivity is not written in stone; it is shaped by our innovations, decisions, and shared aspirations.